In Search for an Ionic Liquid with the Best Performance during 210Pb/210Bi Cherenkov Counting in Waters on an LS Counter
- PMID: 36554442
- PMCID: PMC9778810
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192416563
In Search for an Ionic Liquid with the Best Performance during 210Pb/210Bi Cherenkov Counting in Waters on an LS Counter
Abstract
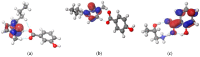
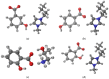
The research presented in this paper aims to investigate the performance of several newly synthesized ionic liquids during 210Pb/210Bi detection in water on a liquid scintillation spectrometer Quantulus 1220 via Cherenkov counting. These experiments have been triggered by the recent reports that certain ionic liquids can act as wavelength shifters, thus significantly increasing the detection efficiency of Cherenkov radiation. The benefit of ionic liquid's addition to the analysed samples is reflected in the detection limit's decrement during 210Pb quantification, which is pertinent considering naturally low levels of 210Pb in aqueous samples. Firstly, it was discovered that ionic liquid, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium salicylate, is more efficient than the previously explored 2-hydroxypropylammonium salicylate. Consequently, the impact of a few other ionic liquids on Cherenkov counting efficiency with the same cation group (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium benzoate, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium 3-hydroxybenzoate and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium 4-hydroxybenzoate) was also explored to test their potential influence. Molecular simulations have been carried out to reveal which structures of ionic liquids assure wavelength-shifting behavior. The obtained results confirmed that, among the investigated ones, only ionic liquids with the salicylate anion exhibited a wavelength shifting effect.
Keywords: 210Pb/210Bi detection; Cherenkov counting; Quantulus 1220; ionic liquids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









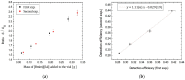

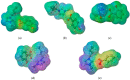




References
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. 4th ed. WHO Press; Genève, Switzerland: 2011.
-
- Murray J.W., Paul B., Dunne J.P., Chapin T. 234Th, 210Pb, 210Po and stable Pb in the central equatorial Pacific: Tracers for particle cycling. Deep-Sea Res. Pt. I. 2005;52:2109–2139. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2005.06.016. - DOI
-
- Kim T.H., Kim G. Important role of colloids in the cycling of 210Po and 210Pb in the ocean: Results from the East/Japan Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2012;95:134–142. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.07.029. - DOI
-
- Larivière D., Reiber K.M., Evans R.D., Cornett R.J. Determination of 210Pb at ultra-trace levels in water by ICP-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2005;549:188–196. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.06.020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

