The Effect of Mother Phubbing on Young Children's Emotional and Behavioral Problems: A Moderated Mediation Model of Mother-Child Attachment and Parenting Stress
- PMID: 36554791
- PMCID: PMC9779429
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192416911
The Effect of Mother Phubbing on Young Children's Emotional and Behavioral Problems: A Moderated Mediation Model of Mother-Child Attachment and Parenting Stress
Abstract
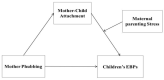
Phubbing-the act of ignoring someone physically present in favor of a mobile phone-is increasingly prevalent in families, and mothers' phubbing behaviors may have a particularly important effect on young children's development. Accordingly, this study explores the mediating role of mother-child attachment in the relationship between mother phubbing and children's emotional and behavioral problems, as well as the role of maternal parenting stress in moderating the mediation effect. A total of 988 mothers of young children (mean age = 4.93, SD = 0.94) were surveyed using four scales, and the resulting data was statistically analyzed. The study found that (1) mother phubbing was significantly and positively correlated with children's emotional and behavioral problems (r = 0.19, p < 0.01), (2) mother-child attachment mediated the relationship between mother phubbing and children's emotional and behavioral problems, and (3) the relationship between mother-child attachment and children's emotional and behavioral problems was moderated by maternal parenting stress. The present study offers fresh evidence of how mother phubbing affects young children's emotional and behavioral difficulties. The need to reduce maternal parental stress and buffer mothers from its effects are highlighted as vital factors in promoting secure mother-child attachment and alleviating young children's problems.
Keywords: emotional and behavioral problems; maternal parenting stress; mother phubbing; mother–child attachment; young children.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The role of mother-child relationship in the association between maternal parenting stress and emotional and behavioral problems in preschool children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Apr 15;25(4):394-400. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2210053. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37073845 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Maternal parenting stress and social-emotional problems of Chinese preschoolers: The role of the mother-child relationship and maternal adverse childhood experiences.J Affect Disord. 2024 Apr 1;350:188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.01.110. Epub 2024 Jan 12. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38220112
-
Parental Phubbing and Children's Social Withdrawal and Aggression: A Moderated Mediation Model of Parenting Behaviors and Parents' Gender.J Interpers Violence. 2022 Nov;37(21-22):NP19395-NP19419. doi: 10.1177/08862605211042807. Epub 2021 Aug 31. J Interpers Violence. 2022. PMID: 34463596
-
Parental Phubbing and Child Social-Emotional Adjustment: A Meta-Analysis of Studies Conducted in China.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023 Oct 19;16:4267-4285. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S417718. eCollection 2023. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023. PMID: 37877136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research review: Effects of parenting programs for children's conduct problems on children's emotional problems - a network meta-analysis.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023 Mar;64(3):348-356. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13697. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36097742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Relationship Between Parental Phubbing and Preschoolers' Behavioral Problems: The Mediation Role of Mindful Attention Awareness.Children (Basel). 2025 Aug 2;12(8):1022. doi: 10.3390/children12081022. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868474 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Phubbing and Problematic Media Use in Preschoolers: The Independent and Interactive Moderating Role of Children's Negative Affectivity and Effortful Control.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024 Aug 27;17:3083-3100. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S471208. eCollection 2024. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024. PMID: 39220633 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of parental psychological flexibility on children's behavioral problems: a moderated mediation model.Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2025 Feb 13;19(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13034-025-00863-y. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 39948671 Free PMC article.
-
Parental Technology Use in a Child's Presence and Health and Development in the Early Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Pediatr. 2025 May 5;179(7):730-7. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2025.0682. Online ahead of print. JAMA Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40323594
References
-
- Chotpitayasunondh V., Douglas K.M. How “phubbing” becomes the norm: The antecedents and consequences of snubbing via smartphone. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016;63:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.018. - DOI
-
- Chotpitayasunondh V., Douglas K.M. The effects of “phubbing” on social interaction. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2018;48:304–316. doi: 10.1111/jasp.12506. - DOI
-
- Roberts J.A., David M.E. Put down your phone and listen to me: How boss phubbing undermines the psychological conditions necessary for employee engagement. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017;75:206–217. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.05.021. - DOI
-
- Roberts J.A., David M.E. My life has become a major distraction from my cell phone: Partner phubbing and relationship satisfaction among romantic partners. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016;54:134–141. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.058. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources