Spatial Distribution Profiles and Human-Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Surrounding Area Surface Soils of a Petrochemical Complex
- PMID: 36554812
- PMCID: PMC9778647
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192416930
Spatial Distribution Profiles and Human-Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Surrounding Area Surface Soils of a Petrochemical Complex
Abstract
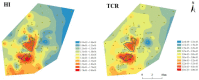
Despite the growing concern raised by organic pollutants from the petrochemical industry to the surrounding soils, the heavy metal (HM) pollution in these soils remains understudied. This study investigated the levels, potential sources, and human-health risks of 12 HMs in soils inside and in surrounding areas of a petrochemical complex. Generally, the levels of 12 HMs in all soil samples were lower than the national standard of China, except for the Cd in one surrounding soil sample. Approximately 40.9% and 98.1% of soils around and inside the petrochemical complex, respectively, were at slightly contaminated levels. The HM pollution in 94.4% of soils inside and 32% of soils in surrounding areas were mainly affected by petrochemical production. Human-health risk showed that although As posed an acceptable cancer risk for adults both in and around the complex, high cancer risk for surrounding children from As was observed. Moreover, around the complex, Cr, Cd, and Pb posed acceptable cancer risks for children, while Cd posed an acceptable cancer risk for adults. The spatial distribution of the health risks decreased with increasing distance from the complex. Overall, our results demonstrate that it is essential to minimize human exposure to HMs originating from the petrochemical industry, especially As, Cr, Cd, and Pb.
Keywords: health risk; heavy metals; petrochemical complex; soil pollution; spatial distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hu B.F., Shao S., Ni H., Fu Z.Y., Hu L.S., Zhou Y., Min X.X., She S.F., Chen S.C., Huang M.X., et al. Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at province level. Environ. Pollut. 2020;266:114961. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114961. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y., Jiang D., Ding D., Wu Y., Wei J., Kong L., Long T., Fan T., Deng S. Ecological-health risks assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around a super-sized lead-zinc smelter with a long production history, in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022;307:119487. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119487. - DOI - PubMed
-
- MEP . Bulletin of National Soil Pollution Survey. MEP: Ministry of Environmental Protection of China; Beijing, China: 2014. (In Chinese)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

