Seasonal Variation Characteristics and the Factors Affecting Plankton Community Structure in the Yitong River, China
- PMID: 36554908
- PMCID: PMC9779663
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192417030
Seasonal Variation Characteristics and the Factors Affecting Plankton Community Structure in the Yitong River, China
Abstract
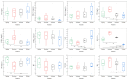
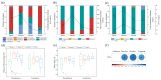
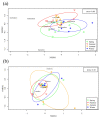
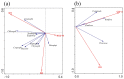
To explore how environmental factors affected the plankton structure in the Yitong River, we surveyed the water environmental factors and plankton population in different seasons. The results showed high total nitrogen concentrations in Yitong River throughout the year, while the total phosphorus, water temperature (WT), and chemical oxygen demand in summer were significantly higher than those in other seasons (p < 0.05), and the dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations and TN/TP ratio were significantly lower (p < 0.01) than those in other seasons. There was no significant seasonal change in other environmental factors. Cyanophyta, Chlorophyta, and Bacillariophyta were the main phytoplankton phylum, while Protozoa and Rotifera were the main zooplankton phylum. The abundance and biomass of zooplankton and phytoplankton in the summer were higher than those in other seasons. Non-Metric Multidimensional scaling methods demonstrated obvious seasonal variation of phytoplankton in summer compared to spring and winter, while the seasonal variation of the zooplankton community was not obvious. The results of the redundancy analysis showed that WT, DO and nitrate nitrogen were the main environmental factors affecting phytoplankton abundance. In contrast to environmental factors, phytoplankton was the main factor driving the seasonal variation of the zooplankton community structure. Cyanophyta were positively correlated with the changes in the plankton community.
Keywords: Cyanophyta; Yitong River; phytoplankton; plankton community; seasonal variation; zooplankton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Serra-Pompei C., Soudijn F., Visser A.W., Kiørboe T., Andersen K.H. A general size-and trait-based model of plankton communities. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020;189:102473. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102473. - DOI
-
- Hattich G.S., Listmann L., Govaert L., Pansch C., Reusch T.B., Matthiessen B. Experimentally decomposing phytoplankton community change into ecological and evolutionary contributions. Funct. Ecol. 2022;36:120–132. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13923. - DOI
-
- van Rensburg S.J., Barnard S., Booyens S. Comparison of phytoplankton assemblages in two differentially polluted streams in the Middle Vaal Catchment, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019;125:234–243. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2019.07.036. - DOI
-
- Zhao K., Bai X., Chen J., Lu H. Assessing the Seasonal Dynamics and Influencing Factors of Phytoplankton Community Structure in Changchun Section of Yitong River. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2021;30:3325–3334.
-
- Lomartire S., Marques J.C., Gonçalves A.M. The key role of zooplankton in ecosystem services: A perspective of interaction between zooplankton and fish recruitment. Ecol. Indic. 2021;129:107867. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107867. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

