Insect-Microorganism Interaction Has Implicates on Insect Olfactory Systems
- PMID: 36555004
- PMCID: PMC9787996
- DOI: 10.3390/insects13121094
Insect-Microorganism Interaction Has Implicates on Insect Olfactory Systems
Abstract
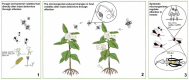
Olfaction plays an essential role in various insect behaviors, including habitat selection, access to food, avoidance of predators, inter-species communication, aggregation, and reproduction. The olfactory process involves integrating multiple signals from external conditions and internal physiological states, including living environments, age, physiological conditions, and circadian rhythms. As microorganisms and insects form tight interactions, the behaviors of insects are constantly challenged by versatile microorganisms via olfactory cues. To better understand the microbial influences on insect behaviors via olfactory cues, this paper summarizes three different ways in which microorganisms modulate insect behaviors. Here, we deciphered three interesting aspects of microorganisms-contributed olfaction: (1) How do volatiles emitted by microorganisms affect the behaviors of insects? (2) How do microorganisms reshape the behaviors of insects by inducing changes in the synthesis of host volatiles? (3) How do symbiotic microorganisms act on insects by modulating behaviors?
Keywords: insect behavior; insect olfactory; microorganism-insect interactions; the olfactory system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insect Odorscapes: From Plant Volatiles to Natural Olfactory Scenes.Front Physiol. 2019 Aug 2;10:972. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00972. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31427985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of olfactory volatiles using gas chromatography-multi-unit recordings (GCMR) in the insect antennal lobe.J Vis Exp. 2013 Feb 24;(72):e4381. doi: 10.3791/4381. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23463015 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial volatile emissions as insect semiochemicals.J Chem Ecol. 2013 Jul;39(7):840-59. doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0306-z. Epub 2013 Jun 23. J Chem Ecol. 2013. PMID: 23793954
-
Microbial interactions shaping host attractiveness: insights into dynamic behavioral relationships.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2024 Dec;66:101275. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2024.101275. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2024. PMID: 39332621 Review.
-
Bacterial volatiles elicit differential olfactory responses in insect species from the same and different trophic levels.Insect Sci. 2023 Oct;30(5):1464-1480. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.13176. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Insect Sci. 2023. PMID: 36644938
Cited by
-
An odorant-binding protein functions in fire ant social immunity interfacing with innate immunity.Open Biol. 2025 Feb;15(2):240254. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240254. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Open Biol. 2025. PMID: 39933575 Free PMC article.
-
Influences of Microbial Symbionts on Chemoreception of Their Insect Hosts.Insects. 2023 Jul 14;14(7):638. doi: 10.3390/insects14070638. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37504644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unusual Genomic and Biochemical Features of Paenarthrobacter lasiusi sp. nov-A Novel Bacterial Species Isolated from Lasius niger Anthill Soil.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 25;26(1):67. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010067. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795926 Free PMC article.
-
The greening-causing agent alters the behavioral and electrophysiological responses of the Asian citrus psyllid to a putative sex pheromone.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):455. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50983-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38172384 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota influences feeding behavior via changes in olfactory receptor gene expression in Colorado potato beetles.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 28;14:1197700. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197700. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37455752 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 32072460/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022A1515012535/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2022ZDZX1044/Research projects in key fields of colleges and universities in Guangdong Province
- 2019TQ05N158/Guangdong Special Branch Plan for Young Talent with Scientific and Technological Innovation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

