Effect of Probiotics on Tenebrio molitor Larval Development and Resistance against the Fungal Pathogen Metarhizium brunneum
- PMID: 36555024
- PMCID: PMC9788617
- DOI: 10.3390/insects13121114
Effect of Probiotics on Tenebrio molitor Larval Development and Resistance against the Fungal Pathogen Metarhizium brunneum
Abstract
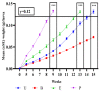
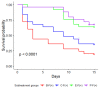
In recent years, the yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) has demonstrated its potential as a mass-produced edible insect for food and feed. However, challenges brought on by pathogens in intensive production systems are unavoidable and require the development of new solutions. One potential solution is the supplementation of probiotics in the insect's diet to obtain the double benefits of improved growth and enhanced immune response. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of diet-based probiotic supplementation on T. molitor larval survival, growth, and resistance against a fungal pathogen. Three probiotic strains, namely Pediococcus pentosacceus KVL-B19-01 isolated from T. molitor and two commercialized strains for traditional livestock, Enterococcus faecium 669 and Bacillus subtilis 597, were tested. Additionally, when larvae were 9 weeks old, a pathogen challenge experiment was conducted with the fungus Metarhizium brunneum. Results showed that both P. pentosaceus and E. faecium improved larval growth and larval survival following fungal exposure compared to the non-supplemented control diet. Since B. subtilis did not improve larval performance in terms of either development or protection against M. brunneum, this study suggests the need for further research and evaluation of probiotic strains and their modes of action when considered as a supplement in T. molitor's diet.
Keywords: disease; immune response; mealworm; probiotics; production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vassileios V. Food waste as a potential new source for edible insect mass production for food and feed: A review. Fermentation. 2019;5:81. doi: 10.3390/fermentation5030081. - DOI
-
- Akhtar Y., Isman M.B. Proteins in Food Processing. 2nd ed. Elsevier Ltd.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Insects as an alternative protein source; pp. 263–288. - DOI
-
- Carus M., Dammer L. The circular bioeconomy—Concepts, opportunities, and limitations. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018;14:83–91. doi: 10.1089/ind.2018.29121.mca. - DOI
-
- Makkar H.P.S., Tran G., Heuzé V., Ankers P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014;197:1–33. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.07.008. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

