Dimethyl Fumarate Alleviates Adult Neurogenesis Disruption in Hippocampus and Olfactory Bulb and Spatial Cognitive Deficits Induced by Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Injection in Young and Aged Rats
- PMID: 36555093
- PMCID: PMC9779626
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415449
Dimethyl Fumarate Alleviates Adult Neurogenesis Disruption in Hippocampus and Olfactory Bulb and Spatial Cognitive Deficits Induced by Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Injection in Young and Aged Rats
Abstract
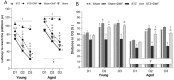
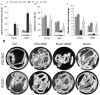
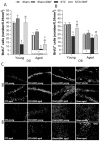
The disorder of adult neurogenesis is considered an important mechanism underlying the learning and memory impairment observed in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The sporadic nonhereditary form of AD (sAD) affects over 95% of AD patients and is related to interactions between genetic and environmental factors. An intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin (STZ-ICV) is a representative and well-established method to induce sAD-like pathology. Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and is used for multiple sclerosis treatment. The present study determines whether a 26-day DMF therapy ameliorates the disruption of adult neurogenesis and BDNF-related neuroprotection in the hippocampus and olfactory bulb (OB) in an STZ-ICV rat model of sAD. Considering age as an important risk factor for developing AD, this study was performed using 3-month-old (the young group) and 22-month-old (the aged group) male Wistar rats. Spatial cognitive functions were evaluated with the Morris water maze task. Immunofluorescent labelling was used to assess the parameters of adult neurogenesis and BDNF-related neuroprotection in the hippocampus and OB. Our results showed that the STZ-ICV evoked spatial learning and memory impairment and disturbances in adult neurogenesis and BDNF expression in both examined brain structures. In the aged animals, the deficits were more severe. We found that the DMF treatment significantly alleviated STZ-ICV-induced behavioural and neuronal disorders in both age groups of the rats. Our findings suggest that DMF, due to its beneficial effect on the formation of new neurons and BDNF-related neuroprotection, may be considered as a promising new therapeutic agent in human sAD.
Keywords: adult neurogenesis; age; dimethyl fumarate; hippocampus; neuroprotection; olfactory bulb; spatial memory impairment; sporadic Alzheimer’s disease; streptozotocin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dimethyl fumarate attenuates intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced spatial memory impairment and hippocampal neurodegeneration in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Jul 15;308:24-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.04.012. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27083302
-
Age-dependent effects of dimethyl fumarate on cognitive and neuropathological features in the streptozotocin-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 2018 May 1;1686:19-33. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29453958
-
The effect of NAD-299 and TCB-2 on learning and memory, hippocampal BDNF levels and amyloid plaques in Streptozotocin-induced memory deficits in male rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Oct;235(10):2809-2822. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4973-x. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30027497
-
Adult neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease.Hippocampus. 2023 Apr;33(4):307-321. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23504. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 36748337 Review.
-
Insight into the role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Feb;84:101828. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101828. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36549424 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Efficacy of Dimethyl Fumarate in Alleviating the Late Streptozotocin-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Neuropathological Features in Rat.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7751-7766. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04024-8. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38430351
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid in an Animal Model of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease Induced by Streptozotocin.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):674-692. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04299-x. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38898198
-
Targeting Neuroinflammation in Central Nervous System Diseases by Oral Delivery of Lipid Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 18;17(3):388. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030388. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40143051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel potential pharmacological applications of dimethyl fumarate-an overview and update.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 7;14:1264842. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1264842. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37745068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoencapsulated Curcumin: Enhanced Efficacy in Reversing Memory Loss in An Alzheimer Disease Model.Brain Sci. 2024 Jan 26;14(2):130. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14020130. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38391705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu H., Rodriguez G.A., Herman M., Emrani S., Nahmani E., Barrett G., Figueroa H.Y., Goldberg E., Hussaini S.A., Duff K.E. Tau Pathology Induces Excitatory Neuron Loss, Grid Cell Dysfunction, and Spatial Memory Deficits Reminiscent of Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron. 2017;93:533–541.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

