Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Pathogenesis and Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment
- PMID: 36555127
- PMCID: PMC9779435
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415489
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Pathogenesis and Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment
Abstract
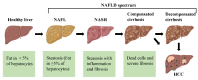
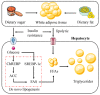
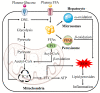
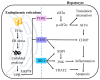
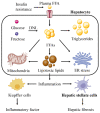
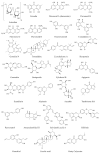
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver disease, affecting approximately one-quarter of the global population, and has become a world public health issue. NAFLD is a clinicopathological syndrome characterized by hepatic steatosis, excluding ethanol and other definite liver damage factors. Recent studies have shown that the development of NAFLD is associated with lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and lipotoxicity. A range of natural products have been reported as regulators of NAFLD in vivo and in vitro. This paper reviews the pathogenesis of NAFLD and some natural products that have been shown to have therapeutic effects on NAFLD. Our work shows that natural products can be a potential therapeutic option for NAFLD.
Keywords: NAFLD; endoplasmic reticulum stress; lipid accumulation; lipotoxicity; natural products; oxidative stress; pathogenesis; plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., Diehl A.M., Brunt E.M., Cusi K., Charlton M., Sanyal A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55:2005–2023. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

