Immunomodulation of HDAC Inhibitor Entinostat Potentiates the Anticancer Effects of Radiation and PD-1 Blockade in the Murine Lewis Lung Carcinoma Model
- PMID: 36555180
- PMCID: PMC9779092
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415539
Immunomodulation of HDAC Inhibitor Entinostat Potentiates the Anticancer Effects of Radiation and PD-1 Blockade in the Murine Lewis Lung Carcinoma Model
Abstract
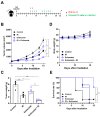
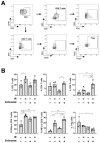
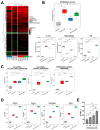
Although the combination of radiotherapy and immunotherapy has proven to be effective in lung cancer treatment, it may not be sufficient to fully activate the antitumor immune response. Here, we investigated whether entinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, could improve the efficacy of radiotherapy and anti-PD-1 in a murine syngeneic LL/2 tumor model. A total of 12 Gy of X-rays administered in two fractions significantly delayed tumor growth in mice, which was further enhanced by oral entinostat administration. Flow cytometry-aided immune cell profiling revealed that entinostat increased radiation-induced infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and CD8+ T cells with decreased regulatory T-cells (Tregs). Transcriptomics-based immune phenotype prediction showed that entinostat potentiated radiation-activated pathways, such as JAK/STAT3/interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and PD-1/PD-L1 signaling. Entinostat augmented the antitumor efficacy of radiation and anti-PD-1, which may be related to an increase in IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T-cells with a decrease in Treg cells. Comparative transcriptomic profiling predicted that entinostat increased the number of dendritic cells, B cells, and T cells in tumors treated with radiation and anti-PD-1 by inducing MHC-II genes. In conclusion, our findings provided insights into how entinostat improves the efficacy of ionizing radiation plus anti-PD-1 therapy and offered clues for developing new strategies for clinical trials.
Keywords: anti-PD-1; antitumor immunity; entinostat; lung cancer; radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tumor-targeted interleukin-12 synergizes with entinostat to overcome PD-1/PD-L1 blockade-resistant tumors harboring MHC-I and APM deficiencies.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jun;10(6):e004561. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004561. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35764364 Free PMC article.
-
Class I histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat suppresses regulatory T cells and enhances immunotherapies in renal and prostate cancer models.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030815. Epub 2012 Jan 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22303460 Free PMC article.
-
Entinostat Neutralizes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Enhances the Antitumor Effect of PD-1 Inhibition in Murine Models of Lung and Renal Cell Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;23(17):5187-5201. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0741. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28698201 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating Histone Deacetylase Signaling Pathways of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Enhanced T Cell-Based Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 24;13:781660. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.781660. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35140716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platinum-based chemotherapy in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: preclinical and clinical studies and mechanism of action.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Feb;18(2):187-203. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2021.1825376. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 32954856 Review.
Cited by
-
HDAC-an important target for improving tumor radiotherapy resistance.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 12;13:1193637. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1193637. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37503317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Epigenetics in Cancer: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Implications.MedComm (2020). 2025 Aug 3;6(8):e70322. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70322. eCollection 2025 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40761481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MS275 induces tumor immunosuppression by upregulating PD-L1 and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in colorectal cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 Mar 17;74(5):150. doi: 10.1007/s00262-025-04004-4. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40095110 Free PMC article.
-
Entinostat Enhances the Efficacy of Chemotherapy in Small Cell Lung Cancer Through S-phase Arrest and Decreased Base Excision Repair.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 14;29(22):4644-4659. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1795. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37725585 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2023 May 20;4(3):e292. doi: 10.1002/mco2.292. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37220590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Spigel D.R., Faivre-Finn C., Gray J.E., Vicente D., Planchard D., Paz-Ares L., Vansteenkiste J.F., Garassino M.C., Hui R., Quantin X., et al. Five-Year Survival Outcomes From the PACIFIC Trial: Durvalumab After Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:1301–1311. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bao L., Diao H., Dong N., Su X., Wang B., Mo Q., Yu H., Wang X., Chen C. Histone deacetylase inhibitor induces cell apoptosis and cycle arrest in lung cancer cells via mitochondrial injury and p53 up-acetylation. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2016;32:469–482. doi: 10.1007/s10565-016-9347-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tang Y.-A., Wen W.-L., Chang J.-W., Wei T.-T., Tan Y.-H.C., Salunke S., Chen C.-T., Chen C.-S., Wang Y.-C. A Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Exhibits Antitumor Activity via Apoptosis Induction, F-Actin Disruption and Gene Acetylation in Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e12417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012417. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

