Fluid Shear Stress Regulates Osteogenic Differentiation via AnnexinA6-Mediated Autophagy in MC3T3-E1 Cells
- PMID: 36555344
- PMCID: PMC9779398
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415702
Fluid Shear Stress Regulates Osteogenic Differentiation via AnnexinA6-Mediated Autophagy in MC3T3-E1 Cells
Abstract
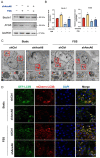
Fluid shear stress (FSS) facilitates bone remodeling by regulating osteogenic differentiation, and extracellular matrix maturation and mineralization. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of how mechanical stimuli from FSS are converted into osteogenesis remain largely unexplored. Here, we exposed MC3T3-E1 cells to FSS with different intensities (1 h FSS with 0, 5, 10, and 20 dyn/cm2 intensities) and treatment durations (10 dyn/cm2 FSS with 0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 h treatment). The results demonstrate that the 1 h of 10 dyn/cm2 FSS treatment greatly upregulated the expression of osteogenic markers (Runx2, ALP, Col I), accompanied by AnxA6 activation. The genetic ablation of AnxA6 suppressed the autophagic process, demonstrating lowered autophagy markers (Beclin1, ATG5, ATG7, LC3) and decreased autophagosome formation, and strongly reduced osteogenic differentiation induced by FSS. Furthermore, the addition of autophagic activator rapamycin to AnxA6 knockdown cells stimulated autophagy process, and coincided with more expressions of osteogenic proteins ALP and Col I under both static and FSS conditions. In conclusion, the findings in this study reveal a hitherto unidentified relationship between FSS-induced osteogenic differentiation and autophagy, and point to AnxA6 as a key mediator of autophagy in response to FSS, which may provide a new target for the treatment of osteoporosis and other diseases.
Keywords: annexinA6; autophagy; fluid shear stress; mineralization; osteogenic differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
miRNA expression profile during fluid shear stress-induced osteogenic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(8):1544-50. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 23595392
-
MiR-20a: a mechanosensitive microRNA that regulates fluid shear stress-mediated osteogenic differentiation via the BMP2 signaling pathway by targeting BAMBI and SMAD6.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jun;10(12):683. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2753. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35845505 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid shear stress stimulates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.J Periodontol. 2014 Dec;85(12):1806-13. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140244. J Periodontol. 2014. PMID: 25186781
-
Combined macromolecule biomaterials together with fluid shear stress promote the osteogenic differentiation capacity of equine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Feb 12;12(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02146-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33579348 Free PMC article.
-
AnnexinA6: a potential therapeutic target gene for extracellular matrix mineralization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 4;11:1201200. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1201200. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37727505 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Taking a closer look at matrix vesicle biogenesis.J Bone Miner Res. 2025 Jul 28;40(8):931-945. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjaf076. J Bone Miner Res. 2025. PMID: 40448594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial strategy for engineering cartilage and bone microtissues using microfluidic cell-laden microgels.Biofabrication. 2025 Apr 22;17(3):10.1088/1758-5090/adc840. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/adc840. Biofabrication. 2025. PMID: 40174602
-
METTL3-mediated m6A modification increases Hspa1a stability to inhibit osteoblast aging.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Mar 27;10(1):155. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01925-4. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38538596 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen promotes bone regeneration by activating the mechanosensitive Piezo1 pathway in osteogenic progenitors.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Jul 25;48:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.07.001. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 39170748 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A5 derived from matrix vesicles protects against osteoporotic bone loss via mineralization.Bone Res. 2023 Nov 9;11(1):60. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00290-9. Bone Res. 2023. PMID: 37940665 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

