TRIB3 Mediates Fibroblast Activation and Fibrosis though Interaction with ATF4 in IPF
- PMID: 36555349
- PMCID: PMC9778945
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415705
TRIB3 Mediates Fibroblast Activation and Fibrosis though Interaction with ATF4 in IPF
Abstract
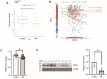
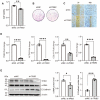
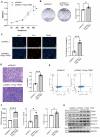
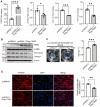
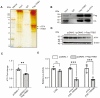
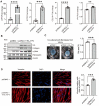
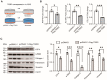
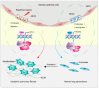
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fatal interstitial lung disease characterized by fibroblast activation, excessive deposition of extracellular matrix, and progressive scarring; the pathogenesis remains elusive. The present study explored the role of Tribbles pseudokinase 3 (TRIB3), a well-known stress and metabolic sensor, in IPF. TRIB3 is down-regulated in the lungs of IPF patients in comparison to control subjects. Deficiency of TRIB3 markedly inhibited A549 epithelial cells' proliferation and migration, significantly reducing wound healing. Conversely, overexpression of TRIB3 promoted A549 cell proliferation and transmigration while it inhibited its apoptosis. Meanwhile, overexpressed TRIB3 inhibited fibroblast activation and decreased ECM synthesis and deposition in MRC5 cells. TRIB3 attenuated pulmonary fibrosis by negative regulation of ATF4, while TRIB3 expression markedly inhibited ATF4 promoter-driven transcription activity and down-regulated ATF4 expression. A co-culture system showed that TRIB3 is important to maintain the normal epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk and regulate fibroblast activation. Taken together, our data suggested that an axis of TRIB3-ATF4 is a key mediator in IPF which might be a potential target for fibroproliferative lung disease treatment.
Keywords: ATF4; TRIB3; epithelial cell; fibroblast activation; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with respect to the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Chen J., Cai Z., Bai M., Yu X., Zhang C., Cao C., Hu X., Wang L., Su R., Wang D., et al. The RNA-binding protein ROD1/PTBP3 cotranscriptionally defines AID-loading sites to mediate antibody class switch in mammalian genomes. Cell Res. 2018;28:981–995. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0076-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnthaler T., Theiler A., Zabini D., Trautmann S., Stacher-Priehse E., Lanz I., Klepetko W., Sinn K., Flick H., Scheidl S., et al. Inhibiting eicosanoid degradation exerts antifibrotic effects in a pulmonary fibrosis mouse model and human tissue. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020;145:818–833.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.032. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

