Hyperpolarization Induced by Lipopolysaccharides but Not by Chloroform Is Inhibited by Doxapram, an Inhibitor of Two-P-Domain K+ Channel (K2P)
- PMID: 36555429
- PMCID: PMC9779748
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415787
Hyperpolarization Induced by Lipopolysaccharides but Not by Chloroform Is Inhibited by Doxapram, an Inhibitor of Two-P-Domain K+ Channel (K2P)
Abstract
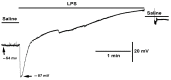
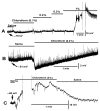
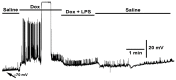
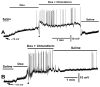
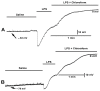
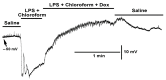
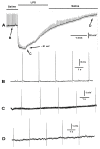
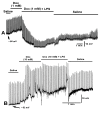
Bacterial septicemia is commonly induced by Gram-negative bacteria. The immune response is triggered in part by the secretion of bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS). LPS induces the subsequent release of inflammatory cytokines which can result in pathological conditions. There is no known blocker to the receptors of LPS. The Drosophila larval muscle is an amendable model to rapidly screen various compounds that affect membrane potential and synaptic transmission such as LPS. LPS induces a rapid hyperpolarization in the body wall muscles and depolarization of motor neurons. These actions are blocked by the compound doxapram (10 mM), which is known to inhibit a subtype of the two-P-domain K+ channel (K2P channels). However, the K2P channel blocker PK-THPP had no effect on the Drosophila larval muscle at 1 and 10 mM. These channels are activated by chloroform, which also induces a rapid hyperpolarization of these muscles, but the channels are not blocked by doxapram. Likewise, chloroform does not block the depolarization induced by doxapram. LPS blocks the postsynaptic glutamate receptors on Drosophila muscle. Pre-exposure to doxapram reduces the LPS block of these ionotropic glutamate receptors. Given that the larval Drosophila body wall muscles are depolarized by doxapram and hyperpolarized by chloroform, they offer a model to begin pharmacological profiling of the K2P subtype channels with the potential of identifying blockers for the receptors to mitigate the actions of the Gram-negative endotoxin LPS.
Keywords: Drosophila; K2P channels; chloroform; doxapram; glutamate receptors; lipopolysaccharides; membrane potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

