Genetic Deletion of AT1a Receptor or Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Selectively in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney Attenuates Two-Kidney, One-Clip Goldblatt Hypertension in Mice
- PMID: 36555438
- PMCID: PMC9779213
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415798
Genetic Deletion of AT1a Receptor or Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Selectively in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney Attenuates Two-Kidney, One-Clip Goldblatt Hypertension in Mice
Abstract
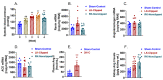
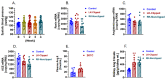
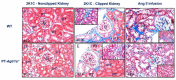
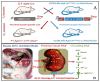
The roles of angiotensin II (Ang II) AT1 (AT1a) receptors and its downstream target Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3) in the proximal tubules in the development of two-kidney, 1-clip (2K1C) Goldblatt hypertension have not been investigated previously. The present study tested the hypothesis that deletion of the AT1a receptor or NHE3 selectively in the proximal tubules of the kidney attenuates the development of 2K1C hypertension using novel mouse models with proximal tubule-specific deletion of AT1a receptors or NHE3. 2K1C Goldblatt hypertension was induced by placing a silver clip (0.12 mm) on the left renal artery for 4 weeks in adult male wild-type (WT), global Agtr1a−/−, proximal tubule (PT)-specific PT-Agtr1a−/− or PT-Nhe3−/− mice, respectively. As expected, telemetry blood pressure increased in a time-dependent manner in WT mice, reaching a maximal response by Week 3 (p < 0.01). 2K1C hypertension in WT mice was associated with increases in renin expression in the clipped kidney and decreases in the nonclipped kidney (p < 0.05). Plasma and kidney Ang II were significantly increased in WT mice with 2K1C hypertension (p < 0.05). Tubulointerstitial fibrotic responses were significantly increased in the clipped kidney (p < 0.01). Whole-body deletion of AT1a receptors completely blocked the development of 2K1C hypertension in Agtr1a−/− mice (p < 0.01 vs. WT). Likewise, proximal tubule-specific deletion of Agtr1a in PT-Agtr1a−/− mice or NHE3 in PT-Nhe3−/− mice also blocked the development of 2K1C hypertension (p < 0.01 vs. WT). Taken together, the present study provides new evidence for a critical role of proximal tubule Ang II/AT1 (AT1a)/NHE3 axis in the development of 2K1C Goldblatt hypertension.
Keywords: 1-clip Goldblatt hypertension; 2-kidney; AT1a receptor; NHE3; angiotensin II; proximal tubule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deletion of AT1a receptors selectively in the proximal tubules of the kidney alters the hypotensive and natriuretic response to atrial natriuretic peptide via NPRA/cGMP/NO signaling.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):F946-F956. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00160.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39361722
-
Sex differences in angiotensin II-induced hypertension and kidney injury: role of AT1a receptors in the proximal tubule of the kidney.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Aug 13;135(15):1825-1843. doi: 10.1042/CS20201574. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34282828 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal Tubule-Specific Deletion of the NHE3 (Na+/H+ Exchanger 3) in the Kidney Attenuates Ang II (Angiotensin II)-Induced Hypertension in Mice.Hypertension. 2019 Sep;74(3):526-535. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13094. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31352824 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II and AT1a Receptors in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney: New Roles in Blood Pressure Control and Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 22;23(5):2402. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052402. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and genomic evidence for an important role of the Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in blood pressure regulation and angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Physiol Genomics. 2019 Apr 1;51(4):97-108. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00122.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Physiol Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30849009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of AT1a receptors selectively in the proximal tubules of the kidney alters the hypotensive and natriuretic response to atrial natriuretic peptide via NPRA/cGMP/NO signaling.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):F946-F956. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00160.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39361722
-
Licochalcone A inhibits glioma migration, invasion, and growth by triggering mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS-mediated oxidative damage.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Aug 6. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05367-z. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40767882
-
Herbal medicine Oryeongsan (Wulingsan): Cardio-renal effects via modulation of renin-angiotensin system and atrial natriuretic peptide system.Integr Med Res. 2024 Sep;13(3):101066. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101066. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Integr Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39247397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics of Hypertensive Nephropathy.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 16;12(11):2622. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12112622. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39595187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carey R.M., Calhoun D.A., Bakris G.L., Brook R.D., Daugherty S.L., Dennison-Himmelfarb C.R., Egan B.M., Flack J.M., Gidding S.S., Judd E., et al. Resistant Hy-pertension: Detection, Evaluation, and Management: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2018;72:e53–e90. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000084. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

