Application of Metabolic Reprogramming to Cancer Imaging and Diagnosis
- PMID: 36555470
- PMCID: PMC9782057
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415831
Application of Metabolic Reprogramming to Cancer Imaging and Diagnosis
Abstract
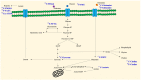
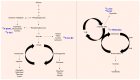
Cellular metabolism governs the signaling that supports physiological mechanisms and homeostasis in an individual, including neuronal transmission, wound healing, and circadian clock manipulation. Various factors have been linked to abnormal metabolic reprogramming, including gene mutations, epigenetic modifications, altered protein epitopes, and their involvement in the development of disease, including cancer. The presence of multiple distinct hallmarks and the resulting cellular reprogramming process have gradually revealed that these metabolism-related molecules may be able to be used to track or prevent the progression of cancer. Consequently, translational medicines have been developed using metabolic substrates, precursors, and other products depending on their biochemical mechanism of action. It is important to note that these metabolic analogs can also be used for imaging and therapeutic purposes in addition to competing for metabolic functions. In particular, due to their isotopic labeling, these compounds may also be used to localize and visualize tumor cells after uptake. In this review, the current development status, applicability, and limitations of compounds targeting metabolic reprogramming are described, as well as the imaging platforms that are most suitable for each compound and the types of cancer to which they are most appropriate.
Keywords: cancer metabolism; cellular uptake; metabolic reprogramming; molecular imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circadian Clocks and Cancer: Timekeeping Governs Cellular Metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Jul;30(7):445-458. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 May 30. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31155396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic rivalry: circadian homeostasis and tumorigenesis.Nat Rev Cancer. 2020 Nov;20(11):645-661. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0291-9. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32895495 Review.
-
Nutrition, metabolism, and epigenetics: pathways of circadian reprogramming.EMBO Rep. 2022 May 4;23(5):e52412. doi: 10.15252/embr.202152412. Epub 2022 Apr 12. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 35412705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Circadian Clock Regulates Metabolic Phenotype Rewiring Via HKDC1 and Modulates Tumor Progression and Drug Response in Colorectal Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2018 Jul;33:105-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 10. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30005951 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging functional roles of nuclear receptors in breast cancer.J Mol Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;58(3):R169-R190. doi: 10.1530/JME-16-0082. Epub 2017 Jan 13. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28087820 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress of Section "Biochemistry" in 2022.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 20;24(6):5873. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065873. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982946 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

