Computational Prediction of Resistance Induced Alanine-Mutation in ATP Site of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
- PMID: 36555475
- PMCID: PMC9784575
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415828
Computational Prediction of Resistance Induced Alanine-Mutation in ATP Site of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors can cause low survival rates in mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer patients. It is necessary to predict new mutations in the development of more potent EGFR inhibitors since classical and rare mutations observed were known to affect the effectiveness of the therapy. Therefore, this research aimed to perform alanine mutagenesis scanning on ATP binding site residues without COSMIC data, followed by molecular dynamic simulations to determine their molecular interactions with ATP and erlotinib compared to wild-type complexes. Based on the result, eight mutations were found to cause changes in the binding energy of the ATP analogue to become more negative. These included G779A, Q791A, L792A, R841A, N842A, V843A, I853A, and D855A, which were predicted to enhance the affinity of ATP and reduce the binding ability of inhibitors with the same interaction site. Erlotinib showed more positive energy among G779A, Q791A, I853A, and D855A, due to their weaker binding energy than ATP. These four mutations could be anticipated in the development of the next inhibitor to overcome the incidence of resistance in lung cancer patients.
Keywords: EGFR; erlotinib; mutation; prediction; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest related to the contents of this research.
Figures
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-alkyl.
, pi-alkyl.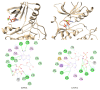
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-sigma;
, pi-sigma;  , pi-sulfur;
, pi-sulfur;  , pi-alkyl.
, pi-alkyl.
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-sulfur;
, pi-sulfur;  , pi-alkyl.
, pi-alkyl.
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-sulfur;
, pi-sulfur;  , pi-alkyl.
, pi-alkyl.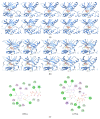
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-sigma;
, pi-sigma;  , pi-alkyl.
, pi-alkyl.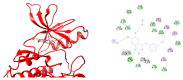
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-alkyl.
, pi-alkyl.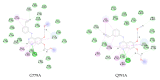
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-sulfur;
, pi-sulfur;  , pi-alkyl).
, pi-alkyl).
 , hydrogen bond;
, hydrogen bond;  , van der Waals;
, van der Waals;  , metal acceptor;
, metal acceptor;  , pi-sulfur;
, pi-sulfur;  , pi-alkyl).
, pi-alkyl).Similar articles
-
Contribution of EGFR and ErbB-3 Heterodimerization to the EGFR Mutation-Induced Gefitinib- and Erlotinib-Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Treatments.PLoS One. 2015 May 20;10(5):e0128360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128360. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25993617 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of sensitivity to gefitinib/erlotinib for EGFR mutations in NSCLC based on structural interaction fingerprints and multilinear principal component analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Mar 7;19(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2093-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29514601 Free PMC article.
-
Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer.Sci Transl Med. 2013 Dec 18;5(216):216ra177. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007205. Sci Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 24353160 Free PMC article.
-
[Indication of EGFR kinase inhibitors should be refined].Klin Onkol. 2011;24(2):87-93. Klin Onkol. 2011. PMID: 21644362 Review. Czech.
-
Acquired resistance of non-small cell lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Respir Investig. 2014 Mar;52(2):82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Respir Investig. 2014. PMID: 24636263 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into fourth generation selective inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR mutation combating non-small cell lung cancer resistance: a critical review.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 21;13(27):18825-18853. doi: 10.1039/d3ra02347h. eCollection 2023 Jun 15. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37350862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
6-Bromo quinazoline derivatives as cytotoxic agents: design, synthesis, molecular docking and MD simulation.BMC Chem. 2024 Jul 4;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01230-2. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38965630 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, design, biological evaluation, and computational analysis of some novel uracil-azole derivatives as cytotoxic agents.BMC Chem. 2024 Jan 3;18(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13065-023-01106-x. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38173035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howlander N., Noone A.M., Krapcho M., Miller D., Brest A., Yu M., Ruhl J., Tatalovich Z., Mariotto A., Lewis D.R., et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018. [(accessed on 11 September 2022)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2018/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

