Red-Emitting Latex Nanoparticles by Stepwise Entrapment of β-Diketonate Europium Complexes
- PMID: 36555596
- PMCID: PMC9785750
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415954
Red-Emitting Latex Nanoparticles by Stepwise Entrapment of β-Diketonate Europium Complexes
Abstract
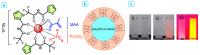
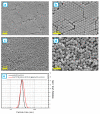
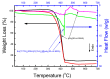
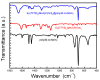
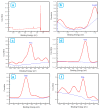
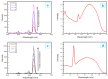
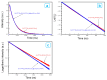
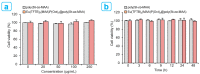
The core-shell structure of poly(St-co-MAA) nanoparticles containing β-diketonate Eu3+ complexes were synthesized by a step-wise process. The β-diketonate Eu3+ complexes of Eu (TFTB)2(MAA)P(Oct)3 [europium (III); 4,4,4-Trifluoro-1-(2-thienyl)-1,3-butanedione = TFTB; trioctylphosphine = (P(Oct)3); methacrylic acid = MAA] were incorporated to poly(St-co-MAA). The poly(St-co-MAA) has highly monodispersed with a size of 300 nm, and surface charges of the poly(St-co-MAA) are near to neutral. The narrow particle size distribution was due to the constant ionic strength of the polymerization medium. The activated carboxylic acid of poly(St-co-MAA) further chelated with europium complex and polymerize between acrylic groups of poly(St-co-MAA) and Eu(TFTB)2(MAA)P(Oct)3. The Em spectra of europium complexes consist of multiple bands of Em at 585, 597, 612 and 650 nm, which are assigned to 5D0→7FJ (J = 0-3) transitions of Eu3+, respectively. The maximum Em peak is at 621 nm, which indicates a strong red Em characteristic associated with the electric dipole 5D0→7F2 transition of Eu3+ complexes. The cell-specific fluorescence of Eu(TFTB)2(MAA)P(Oct)3@poly(St-co-MAA) indicated endocytosis of Eu(TFTB)2(MAA)P(Oct)3@poly(St-co-MAA). There are fewer early apoptotic, late apoptotic and necrotic cells in each sample compared with live cells, regardless of the culture period. Eu(TFTB)2(MAA)P(Oct)3@poly(St-co-MAA) synthesized in this work can be excited in the full UV range with a maximum Em at 619 nm. Moreover, these particles can substitute red luminescent organic dyes for intracellular trafficking and cellular imaging agents.
Keywords: LFIA; europium complex; photoluminescence; polystyrene; β-diketone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
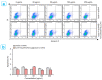
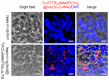
References
-
- Soh J.H., Chan H.-M., Ying J.Y. Strategies for developing sensitive and specific nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays as point-of-care diagnostic device. Nano Today. 2020;30:100831. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2019.100831. - DOI
-
- Khlebtsov B.N., Tumskiy R.S., Burov A.M., Pylaev T.E., Khlebtsov N.G. Quantifying the Numbers of Gold Nanoparticles in the Test Zone of Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strips. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019;2:5020–5028. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00956. - DOI
-
- Goryacheva O.A., Guhrenz C., Schneider K., Beloglazova N.V., Goryacheva I.Y., De Saeger S., Gaponik N. Silanized Luminescent Quantum Dots for the Simultaneous Multicolor Lateral Flow Immunoassay of Two Mycotoxins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020;12:24575–24584. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c05099. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

