Multi-Omics Uncover the Mechanism of Wheat under Heavy Metal Stress
- PMID: 36555610
- PMCID: PMC9785819
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415968
Multi-Omics Uncover the Mechanism of Wheat under Heavy Metal Stress
Abstract
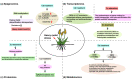
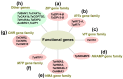
Environmental pollution of heavy metals has received growing attention in recent years. Heavy metals such as cadmium, lead and mercury can cause physiological and morphological disturbances which adversely affect the growth and quality of crops. Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) can accumulate high contents of heavy metals in its edible parts. Understanding wheat response to heavy metal stress and its management in decreasing heavy metal uptake and accumulation may help to improve its growth and grain quality. Very recently, emerging advances in heavy metal toxicity and phytoremediation methods to reduce heavy metal pollution have been made in wheat. Especially, the molecular mechanisms of wheat under heavy metal stress are increasingly being recognized. In this review, we focus on the recently described epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, ionomics and multi-omics combination, as well as functional genes uncovering heavy metal stress in wheat. The findings in this review provide some insights into challenges and future recommendations for wheat under heavy metal stress.
Keywords: functional genes; heavy metal stress; multi-omics; omics; wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A multivariate analysis of physiological and antioxidant responses and health hazards of wheat under cadmium and lead stress.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jan;26(1):362-370. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3605-7. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30397755
-
Heavy metal accumulation in soils and grains, and health risks associated with use of treated municipal wastewater in subsurface drip irrigation.Environ Monit Assess. 2015 Jul;187(7):410. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4565-8. Epub 2015 Jun 7. Environ Monit Assess. 2015. PMID: 26050062
-
Heavy metal accumulation in soil amended with roadside pond sediment and uptake by winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. PBW 343).ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Dec 14;10:2314-29. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.220. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 21170482 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Minimizing Cadmium Accumulation in Wheat.Toxics. 2022 Apr 12;10(4):187. doi: 10.3390/toxics10040187. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35448448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State-of-the-art OMICS strategies against toxic effects of heavy metals in plants: A review.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Sep 1;242:113952. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113952. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 35999767 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics analyses reveal fecal microbial community and metabolic alterations in finishing cattle fed probiotics-fermented distiller's grains diets.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr 11;13(5):e0072124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00721-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40214255 Free PMC article.
-
The Stress Response of Aphids to the Accumulation of Heavy Metals Along Vicia faba L. Under Cadmium Treatment.Insects. 2024 Dec 16;15(12):999. doi: 10.3390/insects15120999. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39769601 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress.Open Life Sci. 2024 Nov 6;19(1):20220953. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0953. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39533982 Free PMC article.
-
Biofortification of Triticum species: a stepping stone to combat malnutrition.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 15;24(1):668. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05161-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39004715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Physiological and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Mechanism of Cd Tolerance in Sinapis alba.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 16;14(12):2224. doi: 10.3390/genes14122224. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38137046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y., Chen Y., Yang Y., Zhang Q., Fu B., Cai J., Guo W., Shi L., Wu J., Chen Y. A thorough screening based on QTLs controlling zinc and copper accumulation in the grain of different wheat genotypes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021;28:15043–15054. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11690-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang S., Tu J., Liu H., Hua M., Liao Q., Feng J., Weng Z., Huang G. Multivariate analysis of trace element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in the Yangtze River Delta, East China. Atmos. Environ. 2009;43:5781–5790. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.07.055. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

