Nucleolar Stress Response via Ribosomal Protein L11 Regulates Topoisomerase Inhibitor Sensitivity of P53-Intact Cancers
- PMID: 36555627
- PMCID: PMC9784028
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415986
Nucleolar Stress Response via Ribosomal Protein L11 Regulates Topoisomerase Inhibitor Sensitivity of P53-Intact Cancers
Abstract
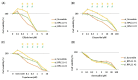
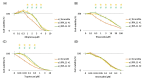
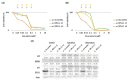
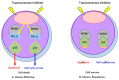
Nucleolar stress response is caused by perturbations in ribosome biogenesis, induced by the inhibition of ribosomal RNA processing and synthesis, as well as ribosome assembly. This response induces p53 stabilization and activation via ribosomal protein L11 (RPL11), suppressing tumor progression. However, anticancer agents that kill cells via this mechanism, and their relationship with the therapeutic efficiency of these agents, remain largely unknown. Here, we sought to investigate whether topoisomerase inhibitors can induce nucleolar stress response as they reportedly block ribosomal RNA transcription. Using rhabdomyosarcoma and rhabdoid tumor cell lines that are sensitive to the nucleolar stress response, we evaluated whether nucleolar stress response is associated with sensitivity to topoisomerase inhibitors ellipticine, doxorubicin, etoposide, topotecan, and anthracyclines. Cell proliferation assay indicated that small interfering RNA-mediated RPL11 depletion resulted in decreased sensitivity to topoisomerase inhibitors. Furthermore, the expression of p53 and its downstream target proteins via western blotting showed the suppression of p53 pathway activation upon RPL11 knockdown. These results suggest that the sensitivity of cancer cells to topoisomerase inhibitors is regulated by RPL11-mediated nucleolar stress responses. Thus, RPL11 expression may contribute to the prediction of the therapeutic efficacy of topoisomerase inhibitors and increase their therapeutic effect of topoisomerase inhibitors.
Keywords: RPL11; drug sensitivity; nucleolar stress response; p53; topoisomerase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
mTOR inhibitors blunt the p53 response to nucleolar stress by regulating RPL11 and MDM2 levels.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(11):1499-514. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.955743. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25482947 Free PMC article.
-
Acrolein preferentially damages nucleolus eliciting ribosomal stress and apoptosis in human cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80450-80464. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12608. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27741518 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of RPL11 at promoter sites of p53-regulated genes upon nucleolar stress through NEDD8 and in an Mdm2-dependent manner.Oncogene. 2012 Jun 21;31(25):3060-71. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.482. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22081073
-
A new PICTure of nucleolar stress.Cancer Sci. 2012 Apr;103(4):632-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02219.x. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22320853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRWD1, a new player among oncogenesis-related ribosomal/nucleolar proteins.Cell Cycle. 2017 Aug 3;16(15):1397-1403. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1338987. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28722511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal insights into ovarian cancer stem cells: revealing the molecular hubs.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jan 31;18(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01597-3. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 39891297 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Pathways in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 5;24(9):8260. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098260. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175967 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar origins: challenging perspectives on evolution and function.Open Biol. 2025 Mar;15(3):240330. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240330. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Open Biol. 2025. PMID: 40068812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Camptothecin Anticancer Drugs with Ribosomal Proteins L15 and L11: A Molecular Docking Study.Molecules. 2023 Feb 15;28(4):1828. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041828. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soren B.C., Babu Dasari J., Ottaviani A., Messina B., Andreotti G., Romeo A., Iacovelli F., Falconi M., Desideri A., Fiorani P. In Vitro and In Silico Characterization of an Antimalarial Compound with Antitumor Activity Targeting Human DNA Topoisomerase IB. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:7455. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147455. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

