Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenases: The Hidden Players of Plant Physiology
- PMID: 36555768
- PMCID: PMC9785579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232416128
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenases: The Hidden Players of Plant Physiology
Abstract
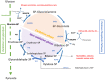
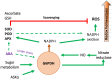
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) catalyzes a metabolic hub between glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), which is the oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) to 6-phosphogluconolactone concomitantly with the production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), a reducing power. It is considered to be the rate-limiting step that governs carbon flow through the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway (OPPP). The OPPP is the main supplier of reductant (NADPH) for several "reducing" biosynthetic reactions. Although it is involved in multiple physiological processes, current knowledge on its exact role and regulation is still piecemeal. The present review provides a concise and comprehensive picture of the diversity of plant G6PDHs and their role in seed germination, nitrogen assimilation, plant branching, and plant response to abiotic stress. This work will help define future research directions to improve our knowledge of G6PDHs in plant physiology and to integrate this hidden player in plant performance.
Keywords: ROS; abiotic stress; apical dominance; glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; seed germination; sugar signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Copeland L.E.S., Turner J.F. Biochemistry of Metabolism. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1987. The Regulation of Glycolysis and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway; pp. 107–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

