Correlation of Biomarkers of Endothelial Injury and Inflammation to Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 36556051
- PMCID: PMC9785942
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11247436
Correlation of Biomarkers of Endothelial Injury and Inflammation to Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
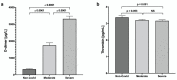
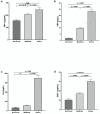
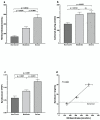
COVID-19 can trigger an intense systemic inflammation and prothrombotic state, leading to a rapid and disproportionate deterioration of lung function. An effective screening tool is essential to identify the patients at risk for severe disease. This observational study was conducted on hospitalized patients with moderate and severe COVID-19 pneumonia in a general hospital in Mexico City between 1 March 2021 and 15 March 2021. Serum samples were analyzed to explore the role of biomarkers of inflammation, coagulation, oxidative stress, and endothelial damage with the severity of the disease. Our results demonstrated that Syndecan-1 and nitrites/nitrates showed a high correlation in severely ill patients. In conclusion, COVID-19 patients with elevated levels of SDC-1 were associated with severe disease. This molecule can potentially be used as a marker for the progression or severity of COVID-19. Preservation of glycocalyx integrity may be a potential treatment for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; endothelial injury; inflammatory biomarkers; syndecan-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Francisco Villarreal (Founder) and Guillermo Ceballos are stockholders of Epirium Bio Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indications of Persistent Glycocalyx Damage in Convalescent COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis.Viruses. 2021 Nov 21;13(11):2324. doi: 10.3390/v13112324. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34835130 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecan-1, an indicator of endothelial glycocalyx degradation, predicts outcome of patients admitted to an ICU with COVID-19.Mol Med. 2021 Dec 3;27(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00412-1. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34861818 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma biomarkers of endothelial function, inflammation and oxidative stress in individuals with non-freezing cold injury.Exp Physiol. 2023 Mar;108(3):448-464. doi: 10.1113/EP090722. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Exp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36808666 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Glycocalyx Injury and Endothelial Activation are Associated with Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Intensive Care Med. 2023 Jan;38(1):95-105. doi: 10.1177/08850666221109186. Epub 2022 Jun 19. J Intensive Care Med. 2023. PMID: 35722738
-
Vascular Endothelial Glycocalyx Damage in COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 19;21(24):9712. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249712. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33352699 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 uptake and inflammatory response in senescent endothelial cells are regulated by the BSG/VEGFR2 pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 5;122(31):e2502724122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2502724122. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40720650 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic strategies targeting the endothelial glycocalyx.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2023 Nov 1;26(6):543-550. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000973. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2023. PMID: 37555800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MixOmics Integration of Biological Datasets Identifies Highly Correlated Variables of COVID-19 Severity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 15;26(10):4743. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104743. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429886 Free PMC article.
-
Endotheliopathy in Acute COVID-19 and Long COVID.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 4;24(9):8237. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098237. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175942 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acids, post-translational modifications, nitric oxide, and oxidative stress in serum and urine of long COVID and ex COVID human subjects.Amino Acids. 2023 Sep;55(9):1173-1188. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03305-1. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Amino Acids. 2023. PMID: 37516715 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

