The Penn Medicine BioBank: Towards a Genomics-Enabled Learning Healthcare System to Accelerate Precision Medicine in a Diverse Population
- PMID: 36556195
- PMCID: PMC9785650
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12121974
The Penn Medicine BioBank: Towards a Genomics-Enabled Learning Healthcare System to Accelerate Precision Medicine in a Diverse Population
Abstract
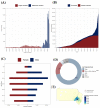
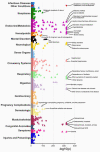
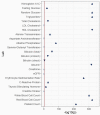
The Penn Medicine BioBank (PMBB) is an electronic health record (EHR)-linked biobank at the University of Pennsylvania (Penn Medicine). A large variety of health-related information, ranging from diagnosis codes to laboratory measurements, imaging data and lifestyle information, is integrated with genomic and biomarker data in the PMBB to facilitate discoveries and translational science. To date, 174,712 participants have been enrolled into the PMBB, including approximately 30% of participants of non-European ancestry, making it one of the most diverse medical biobanks. There is a median of seven years of longitudinal data in the EHR available on participants, who also consent to permission to recontact. Herein, we describe the operations and infrastructure of the PMBB, summarize the phenotypic architecture of the enrolled participants, and use body mass index (BMI) as a proof-of-concept quantitative phenotype for PheWAS, LabWAS, and GWAS. The major representation of African-American participants in the PMBB addresses the essential need to expand the diversity in genetic and translational research. There is a critical need for a "medical biobank consortium" to facilitate replication, increase power for rare phenotypes and variants, and promote harmonized collaboration to optimize the potential for biological discovery and precision medicine.
Keywords: PMBB; biobank; electronic health records; genomics; learning health system; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
SMD receives research funding from RenalytixAI, in-kind research support from Novo Nordisk, and personal consulting fees from Calico Labs. DJR serves on scientific advisory boards for Alnylam, Novartis, Pfizer, and Verve. Regeneron has generated genomic data in PMBB participants. These entities had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of this manuscript; or in the decision to publish these results.
Figures


References
-
- Institute of Medicine . Genomics-Enabled Learning Health Care Systems: Gathering and Using Genomic Information to Improve Patient Care and Research: Workshop Summary. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC, USA: 2015. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

