Diabetes Patients' Acceptance of Injectable Treatment, a Scientometric Analysis
- PMID: 36556420
- PMCID: PMC9782907
- DOI: 10.3390/life12122055
Diabetes Patients' Acceptance of Injectable Treatment, a Scientometric Analysis
Abstract
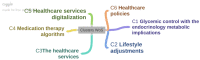
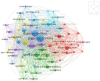
Diabetes is a condition associated with multiple systemic secondary risk factors, besides pancreatic dysfunctions, affecting the population worldwide and with high costs impacting the healthcare systems. This paper aims to identify the major issues in patients' adherence to injectable diabetes treatment. After the interrogation of the Web of Science database, a scientometric map was generated, from which six directions of approach were identified as essential factors influencing the patient's adherence. These directions yielded clusters of related articles. Glycemic control with the endocrinology metabolic implications, lifestyle adjustments, the healthcare services, medication therapy algorithm, healthcare services digitalization and healthcare policies seem to have a major impact on injectable diabetes therapy and patient adherence. Further research on every one of the six directions is needed to identify the potential of increasing injectable treatment adherence in diabetes patients.
Keywords: adherence; compliance; diabetes; diabetes mellitus; injectable treatment; insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Romero-Castillo R., Pabón-Carrasco M., Jiménez-Picón N., Ponce-Blandón J.A. Effects of Nursing Diabetes Self-Management Education on Glycemic Control and Self-Care in Type 1 Diabetes: Study Protocol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;19:5079. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095079. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Togo A., Minkailou M., Trebuchet P., Sylla D., Sidibé A.T., Besançon S., Nguemeni M., Signe T., Lab B., Castellsague M. Éducation thérapeutique au Mali: Un atelier de formation pour soignants et jeunes diabétiques de type 1. Méd. Trop. St. Int. 2021;1:136. doi: 10.48327/MTSIBULLETIN.2021.136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peña A., Olson M.L., Hooker E., Ayers S.L., Castro F.G., Patrick D.L., Corral L. Effects of a Diabetes Prevention Program on Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors and Quality of Life Among Latino Youths with Prediabetes A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open. 2022;5:1–13. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources