Molecular Characterization and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing of a Collagen Gene, Me-col-1, in Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii
- PMID: 36556467
- PMCID: PMC9784238
- DOI: 10.3390/life12122103
Molecular Characterization and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing of a Collagen Gene, Me-col-1, in Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii
Abstract
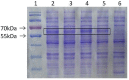
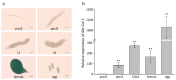
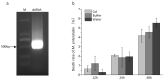
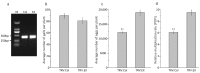
Meloidogyne enterolobii, a highly pathogenic root-knot nematode species, causes serious damage to agricultural production worldwide. Collagen is an important part of the nematode epidermis, which is crucial for nematode shape maintenance, motility, and reproduction. In this study, we report that a novel collagen gene, Me-col-1, from the highly pathogenic root-knot nematode species Meloidogyne enterolobi was required for the egg formation of this pathogen. Me-col-1 encodes a protein with the size of 35 kDa, which is closely related to collagen found in other nematodes. Real-time PCR assays showed that the expression of Me-col-1 was highest in eggs and lowest in pre-parasitic second-stage juveniles (preJ2). Interestingly, knockdown of Me-col-1 did not compromise the survival rate of preJ2 but significantly reduced the egg production and consequentially caused 35.79% lower multiplication rate (Pf/Pi) compared with control. Our study provides valuable information for better understanding the function of collagen genes in the nematode life cycle, which can be used in the development of effective approaches for nematode control.
Keywords: Meloidogyne enterolobii; RNAi; VIGS; collagens; root-knot nematode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct Genomic Loci Underlie Quantitative Resistance to Meloidogyne enterolobii Galling and Reproduction in Citrullus amarus.Plant Dis. 2023 Jul;107(7):2126-2132. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-22-2228-RE. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Plant Dis. 2023. PMID: 36548923
-
Evaluation of nematicides for Meloidogyne enterolobii management in sweetpotato.J Nematol. 2024 Aug 24;56(1):20240033. doi: 10.2478/jofnem-2024-0033. eCollection 2024 Mar. J Nematol. 2024. PMID: 39221106 Free PMC article.
-
Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Variations in Tomatoes after Infection with Different Density Levels of Meloidogyne enterolobii.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 18;13(2):293. doi: 10.3390/plants13020293. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256846 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome reveals the roles and potential mechanisms of lncRNAs in the regulation of albendazole resistance in Haemonchus contortus.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 17;25(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10096-6. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38368335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rutter W.B., Skantar A.M., Handoo Z.A., Mueller J.D., Aultman S.P., Agudelo P. Meloidogyne enterolobii Found Infecting Root-Knot Nematode Resistant Sweetpotato in South Carolina, United States. Plant Dis. 2019;103:775. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-18-1388-PDN. - DOI
-
- Collett R., Marais M., Daneel M., Rashidifard M., Fourie H. Meloidogyne enterolobii, a threat to crop production with particular reference to sub-Saharan Africa: An extensive, critical and updated review. Nematology. 2021:1–39. doi: 10.1163/15685411-bja10076. - DOI
-
- Santos D., Abrantes I., Maleita C. The quarantine root-knot nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii—A potential threat to Portugal and Europe. Plant Pathol. 2019;68:1607–1615. doi: 10.1111/ppa.13079. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

