Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods
- PMID: 36556665
- PMCID: PMC9782874
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15248857
Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods
Abstract
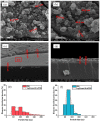
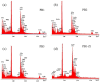
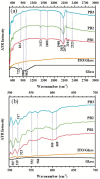
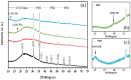
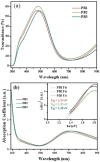
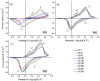
Prussian Blue (PB) thin films were prepared by DC chronoamperometry (CHA), symmetric pulse, and non-symmetric pulse electrodeposition techniques. The formation of PB was confirmed by infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and UV-Vis transmission measurements. X-ray diffraction (XRD) shows the stabilization of the insoluble form of PB. From scanning electron microscopy (SEM) studies, an increase in porosity is obtained for the shorter pulse widths, which tends to improve the total charge exchange and electrochemical stability of the films. While the film prepared by CHA suffered a degradation of 82% after 260 cycles, the degradation reduced to 24% and 34% for the samples prepared by the symmetric and non-symmetric pulse methods, respectively. Additionally, in the non-symmetric pulse film, the improvement in the charge exchange reached ~522% after 260 cycles. According to this study, the deposition time distribution affects the physical/chemical properties of PB films. These results then render pulse electrodeposition methods especially suitable to produce high-quality thin films for electrochemical devices, based on PB.
Keywords: Prussian blue; charge exchange; electrochemical devices; electrochemical stability; pulse electrodeposition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films.Materials (Basel). 2019 Apr 3;12(7):1103. doi: 10.3390/ma12071103. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30987083 Free PMC article.
-
Photoelectrocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue on Electrodeposited Bismuth Ferrite Perovskite Films.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;16(7):2769. doi: 10.3390/ma16072769. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37049063 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and electrochemical investigation of layer-by-layer deposited titanium phosphate/Prussian blue composite films.Langmuir. 2007 May 22;23(11):6084-90. doi: 10.1021/la700239r. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Langmuir. 2007. PMID: 17439262
-
In Situ Electrodeposition of Pb and Ag Applied on Fluorine Doped Tin Oxide Substrates: Comparative Experimental and Theoretical Study.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;15(24):8865. doi: 10.3390/ma15248865. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556671 Free PMC article.
-
Epitaxial electrodeposition of Prussian blue thin films on single-crystal Au(110).J Am Chem Soc. 2003 Dec 10;125(49):14998-9. doi: 10.1021/ja0381151. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 14653729
Cited by
-
Long-term performance of low-cost free chlorine sensors to monitor on-site water reuse.Water Sci Technol. 2025 Jul;92(2):326-339. doi: 10.2166/wst.2025.090. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Water Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40739827
References
-
- Monk P.M., Mortimer R.J., Rosseinsky D.R. Electrochromism and Electrochromic Devices. Volume 421 Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2007.
-
- Isfahani V.B., Memarian N., Dizaji H.R., Arab A., Silva M.M. The physical and electrochromic properties of Prussian Blue thin films electrodeposited on ITO electrodes. Electrochim. Acta. 2019;304:282–291. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.02.120. - DOI
-
- Isfahani V.B., Pereira R.F., Fernandes M., Sabadini R.C., Pereira S., Dizaji H.R., Arab A., Fortunato E., Pawlicka A., Rego R. Gellan-Gum and LiTFSI-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Electrochromic Devices. ChemistrySelect. 2021;6:5110–5119. doi: 10.1002/slct.202004614. - DOI
-
- Yi H., Qin R., Ding S., Wang Y., Li S., Zhao Q., Pan F. Structure and properties of prussian blue analogues in energy storage and conversion applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2006970. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202006970. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

