In Situ Electrodeposition of Pb and Ag Applied on Fluorine Doped Tin Oxide Substrates: Comparative Experimental and Theoretical Study
- PMID: 36556671
- PMCID: PMC9781746
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15248865
In Situ Electrodeposition of Pb and Ag Applied on Fluorine Doped Tin Oxide Substrates: Comparative Experimental and Theoretical Study
Abstract
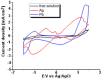
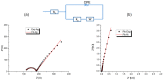
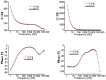
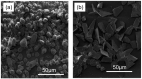
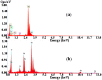
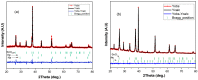
A comparison between lead and silver electrodeposition onto fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) electrodes from nitrate solution was investigated in this work. Chronoamperometry has been used as an in situ technique to track the dynamics of the electrodeposition during advanced nucleation phases. The experimental results are correlated with a theoretical evaluation. It has shown that they have a strong correlation with each other. After that, the obtained deposits are characterized and compared as well by X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and impedance spectroscopy. The data reflects the effect of the material under investigation on current density, deposition density, and dielectric properties. Additionally, the electrodeposition approach (a two-in-one technique) can be followed in order to make well-controlled thin films that can be used for various purposes in addition to recovering heavy metals from wastewater.
Keywords: X-ray diffraction FTO; impedance spectroscopy; in situ electrodeposition; lead; silver.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Physical, Static, and Kinetic Analysis of the Electrochemical Deposition Process for the Recovery of Heavy Metal from Industrial Wastewater.Scientifica (Cairo). 2023 Jan 7;2023:2741586. doi: 10.1155/2023/2741586. eCollection 2023. Scientifica (Cairo). 2023. PMID: 36647551 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of WO3 Electrodeposition Leading to Nanostructured Thin Films.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;10(8):1493. doi: 10.3390/nano10081493. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751424 Free PMC article.
-
Electrodeposition of Cu2NiSnS4 absorber layer on FTO substrate for solar cell applications.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 18;14(40):29439-29454. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04249b. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39297033 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;15(24):8857. doi: 10.3390/ma15248857. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556665 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Electrosynthesis Potential on Nucleation, Growth, Adhesion, and Electronic Properties of Polypyrrole Thin Films on Fluorine-Doped Tin Oxide (FTO).Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jul 23;13(15):2419. doi: 10.3390/polym13152419. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34372020 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Physical, Static, and Kinetic Analysis of the Electrochemical Deposition Process for the Recovery of Heavy Metal from Industrial Wastewater.Scientifica (Cairo). 2023 Jan 7;2023:2741586. doi: 10.1155/2023/2741586. eCollection 2023. Scientifica (Cairo). 2023. PMID: 36647551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sangkarak S., Phetrak A., Kittipongvises S., Kitkaew D., Phihusut D., Lohwacharin J. Adsorptive Performance of Activated Carbon Reused from Household Drinking Water Filter for Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Water. J. Environ. Manag. 2020;272:111085. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111085. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wood D.M., Greenland B.W., Acton A.L., Rodríguez-Llansola F., Murray C.A., Cardin C.J., Miravet J.F., Escuder B., Hamley I.W., Hayes W. PH-Tunable Hydrogelators for Water Purification: Structural Optimisation and Evaluation. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2012;18:2692–2699. doi: 10.1002/chem.201102137. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Savage N., Diallo M.S. Nanomaterials and Water Purification: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Nanopart. Res. 2005;7:331–342. doi: 10.1007/s11051-005-7523-5. - DOI
-
- Singh N.B., Nagpal G., Agrawal S. Water Purification by Using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018;11:187–240. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

