Effects of Molarity and Storage Time of MWCNTs on the Properties of Cement Paste
- PMID: 36556845
- PMCID: PMC9785388
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15249035
Effects of Molarity and Storage Time of MWCNTs on the Properties of Cement Paste
Abstract
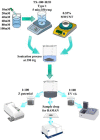
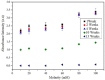
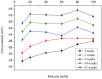
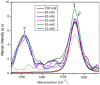
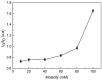
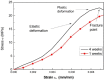
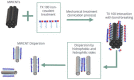
Nowadays, nanomaterials in cement pastes are among the most important topics in the cement industry because they can be used for several applications. For this reason, this work presents a study about the influence of changing the molarity of dispersed multiple wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and varying the number of storage days on the mechanical properties of the cement paste. To achieve this objective, dispersions of 0.35% MWCNTs, varying the molarity of the surfactant as 10 mM, 20 mM, 40 mM, 60 mM, 80 mM, and 100 mM, were performed. The mixture of materials was developed using the sonication process; furthermore, materials were analyzed using UV-Vis, Z-potential, and Raman spectroscopy techniques. Materials with a molarity of 10 mM exhibited the best results, allowing them to also be stored for four weeks. Regarding the mechanical properties, an increase in the elastic modulus was observed when MWCNTs were included in the cement paste for all storage times. The elastic modulus and the maximum stress increased as the storage time increased.
Keywords: MWCNT; cement paste; dispersion; sonication energy; stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Liu J., Liu L., Lu J., Zhu H. The formation mechanism of chiral carbon nanotubes. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2018;530:277–282. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2017.11.068. - DOI
-
- Oliveira T.M.B.F., Morais S. New Generation of Electrochemical Sensors Based on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Appl. Sci. 2018;8:1925. doi: 10.3390/app8101925. - DOI
-
- Zaporotskova I.V., Boroznina N.P., Parkhomenko Y.N., Kozhitov L.V. Carbon nanotubes: Sensor properties. A review. Mod. Electron. Mater. 2016;2:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.moem.2017.02.002. - DOI
-
- Bortz D.R., Merino C., Martin-Gullon I. Carbon nanofibers enhance the fracture toughness and fatigue performance of a structural epoxy system. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011;71:31–38. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.09.015. - DOI
-
- Senff L., Modolo R., Tobaldi D., Ascenção G., Hotza D., Ferreira V., Labrincha J. The influence of TiO2 nanoparticles and poliacrilonitrile fibers on the rheological behavior and hardened properties of mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015;75:315–330. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.11.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

