Non-Volatile Memory and Synaptic Characteristics of TiN/CeOx/Pt RRAM Devices
- PMID: 36556891
- PMCID: PMC9786700
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15249087
Non-Volatile Memory and Synaptic Characteristics of TiN/CeOx/Pt RRAM Devices
Abstract
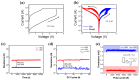
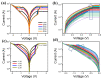
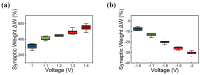
In this study, we investigate the synaptic characteristics and the non-volatile memory characteristics of TiN/CeOx/Pt RRAM devices for a neuromorphic system. The thickness and chemical properties of the CeOx are confirmed through TEM, EDS, and XPS analysis. A lot of oxygen vacancies (ions) in CeOx film enhance resistive switching. The stable bipolar resistive switching characteristics, endurance cycling (>100 cycles), and non-volatile properties in the retention test (>10,000 s) are assessed through DC sweep. The filamentary switching model and Schottky emission-based conduction model are presented for TiN/CeOx/Pt RRAM devices in the LRS and HRS. The compliance current (1~5 mA) and reset stop voltage (−1.3~−2.2 V) are used in the set and reset processes, respectively, to implement multi-level cell (MLC) in DC sweep mode. Based on neural activity, a neuromorphic system is performed by electrical stimulation. Accordingly, the pulse responses achieve longer endurance cycling (>10,000 cycles), MLC (potentiation and depression), spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP), and excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) to mimic synapse using TiN/CeOx/Pt RRAM devices.
Keywords: cerium oxide; memristor; neuromorphic system; resistive switching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang Z., Wang Z., Shi T., Bi C., Rao F., Cai Y., Liu Q., Wu H., Zhou P. Memory Materials and Devices: From Concept to Application. InfoMat. 2020;2:261–290. doi: 10.1002/inf2.12077. - DOI
-
- Atzori L., Iera A., Morabito G. The Internet of Things: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2010;54:2787–2805. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.010. - DOI
-
- Lin Y., Zeng T., Xu H., Wang Z., Zhao X., Liu W., Ma J., Liu Y. Transferable and Flexible Artificial Memristive Synapse Based on WOx Schottky Junction on Arbitrary Substrates. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018;4:1800373. doi: 10.1002/aelm.201800373. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

