Effect of Dupilumab on Sexual Desire in Adult Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis
- PMID: 36556910
- PMCID: PMC9782472
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58121708
Effect of Dupilumab on Sexual Desire in Adult Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
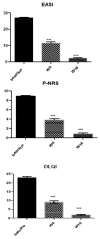
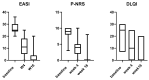
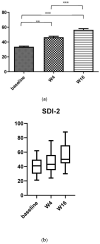
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory condition causing itching skin, with a significant psychosocial impact on patients and relatives. AD affects 15 to 30% of children and 2 to 10% of adults. AD significantly affects patients' quality of life (QoL) given the chronicity and symptoms of the disease. Most AD patients have reported that the disease affects daily life, resulting in limited social contact and a strong impact on sexual health (SH), especially in moderate-severe cases. Materials and methods: We performed a prospective study from 1 May 2020 to 1 May 2022; the aim of the study was to evaluate the impact of moderate to severe AD on sexual desire, seduction, and partner relationships, and describe how it varies following dupilumab therapy. We used the Sexual Desire Inventory-2 (SDI-2), a validated instrument consisting of 14 items; moreover, we used a second questionnaire with eight items, an unvalidated instrument created specifically for this study, to obtain the assessment of the influence of AD on the body image, sexuality, and self-perception of those affected. Results and Conclusions: The impact of AD on sexual desire assessed using SDI-2 showed a significant improvement in both sexes during dupilumab treatment from the baseline to W4 and W16. Similar results were obtained with our questionnaire.
Keywords: SDI-2; atopic dermatitis; sexual disfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
M.N. has acted as speaker, consultant, and advisory board member for Sanofi, Abbvie, Leo Pharma, Novartis, and EliLilly; G.F. has served as the principal investigator in clinical trials sponsored by and/or and has received personal fees from AbbVie, Abiogen, Almirall, Celgene, EliLilly, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and UCB; C.P. has acted as investigator, speaker, consultant, and advisory board member for AbbVie, Amgen, EliLilly, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, and Sanofi. The other authors declare to not have any conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improvement of Sexual Function and Sleep Quality in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Dupilumab: A Single-Centre Prospective Observational Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 20;20(3):1918. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031918. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767285 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab improves patient-reported symptoms of atopic dermatitis, symptoms of anxiety and depression, and health-related quality of life in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: analysis of pooled data from the randomized trials SOLO 1 and SOLO 2.J Dermatolog Treat. 2020 Sep;31(6):606-614. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1612836. Epub 2019 Jun 9. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020. PMID: 31179791 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinically Meaningful Responses to Dupilumab in Adolescents with Uncontrolled Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Post-hoc Analyses from a Randomized Clinical Trial.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020 Feb;21(1):119-131. doi: 10.1007/s40257-019-00478-y. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31823222 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dupilumab: A review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Mar;78(3 Suppl 1):S28-S36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29471919 Review.
-
Assessing the need for routine safety testing for patients being treated with dupilumab for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jun;182(6):e186-e209. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19065. Br J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32476149 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Mediated Skin Diseases: Future Therapeutic Perspectives.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 8;59(10):1787. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101787. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893505 Free PMC article.
-
Atopic Dermatitis And Intercourse Difficulties : A Cross-sectional Study of the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966 Study.Acta Derm Venereol. 2025 Jan 3;105:adv40785. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v105.40785. Acta Derm Venereol. 2025. PMID: 39750038 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Global prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women with skin diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12905-025-03625-2. BMC Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40050796 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of Sexual Function and Sleep Quality in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Dupilumab: A Single-Centre Prospective Observational Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 20;20(3):1918. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031918. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767285 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dysfunction in Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 10;14(8):2602. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082602. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sampogna F., Abeni D., Gieler U., Tomas-Aragones L., Lien L., Titeca G., Jemec G., Misery L., Szabó C., Linder M., et al. Impairment of Sexual Life in 3485 Dermatological Outpatients From a Multicentre Study in 13 European Countries. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017;97:478–482. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2561. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

