The RAAS Axis and SARS-CoV-2: From Oral to Systemic Manifestations
- PMID: 36556919
- PMCID: PMC9784172
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58121717
The RAAS Axis and SARS-CoV-2: From Oral to Systemic Manifestations
Abstract
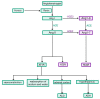
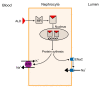
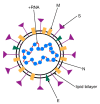
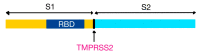
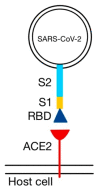
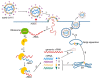
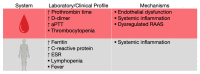
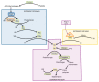
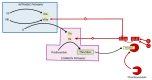
One of the essential regulators of arterial blood pressure, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) seems to be one of the most complex mechanisms in the human body. Since the discovery of its key components and their actions, new substances and functions are still being unraveled. The main pathway begins with the secretion of renin in the kidney and culminates with the synthesis of angiotensin II (Ang II)-a strong vasoconstrictor-thanks to the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Research conducted in 2000 identified another enzyme, named ACE2, that converts Ang II into Ang-(1-7), a heptapeptide with opposing effects to those of Ang II: vasodilation and anti-inflammatory properties. This particular enzyme became of paramount importance during the last two decades, as a result of the confrontation of the human race with life-threatening epidemics. Multiple studies have been performed in order to uncover the link between ACE2 and human coronaviruses, the results of which we systemized in order to create an overview of the pathogenic mechanism. Human coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, attach to ACE2 via their spike proteins (S), causing the destruction of the enzyme. Because ACE2 limits the production of Ang II (by converting it into Ang-(1-7)), its destruction leads to a dysregulated inflammatory response. The purpose of this review is to decipher the complex pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the multiorgan complications (oral, cardiac, pulmonary, systemic) that appear as a result of the interaction of the SARS CoV-2 virus with the angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; RAAS; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The interacting physiology of COVID-19 and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Key agents for treatment.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Feb;10(1):e00917. doi: 10.1002/prp2.917. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35106954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Renin Angiotensin Axis, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 and Coronavirus].Rev Chil Pediatr. 2020 Jun;91(3):330-338. doi: 10.32641/rchped.vi91i3.2548. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32730512 Review. Spanish.
-
A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm.Elife. 2020 Jul 7;9:e59177. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59177. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32633718 Free PMC article.
-
The spike effect of acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and coronavirus disease 2019 vaccines on blood pressure.Eur J Intern Med. 2023 Mar;109:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2022.12.004. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Eur J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36528504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 and Renin-Angiotensin Peptides in SARS-CoV-2 Mediated Mortality and End-Organ Injuries.Hypertension. 2022 Feb;79(2):365-378. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18295. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 34844421
Cited by
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 14;12(3):583. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030583. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Are at Greater Risk of Developing New Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease Following COVID-19.J Diabetes Res. 2025 Jun 4;2025:8816198. doi: 10.1155/jdr/8816198. eCollection 2025. J Diabetes Res. 2025. PMID: 40503239 Free PMC article.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System: The Challenge behind Autoimmune Dermatological Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 7;13(22):3398. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223398. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boron W.F., Boulpaep E.L. Medical Physiology: A Cellular and Molecular Approach. 2nd ed. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2012.
-
- Donoghue M., Hsieh F., Baronas E., Godbout K., Gosselin M., Stagliano N., Donovan M., Woolf B., Robison K., Jeyaseelan R., et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.87.5.e1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hall J.E. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2011.
-
- Ross M.H., Pawlina W. Histology: A Text and Atlas. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

