Dinebra retroflexa Herbal Phytotherapy: A Simulation Study Based on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Retraction Potential in Swiss Albino Rats
- PMID: 36556921
- PMCID: PMC9782064
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58121719
Dinebra retroflexa Herbal Phytotherapy: A Simulation Study Based on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Retraction Potential in Swiss Albino Rats
Abstract
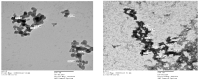
Background and Objectives: Fibrotic lung disease is one of the main complications of many medical conditions. Therefore, the use of anti-fibrotic agents may provide a chance to prevent, or at least modify, such complication. The aim of this study was to evaluate the protective pulmonary anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects of Dinebra retroflexa. Materials and methods: Dinebra retroflexa methanolic extract and its synthesized silver nanoparticles were tested on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Pulmonary fibrosis was induced by intratracheal instillation of bleomycin (5 mg/5 mL/kg-Saline) as a supposed model for induced lung fibrosis. The weed evaluation was performed by intratracheal instillation of Dinebra retroflexa methanolic extract and its silver nanoparticles (35 mg/100 mL/kg-DMSO, single dose). Results: The results showed that both Dinebra retroflexa methanolic extract and its silver nanoparticles had a significant pulmonary fibrosis retraction potential, with Ashcroft scores of three and one, respectively, and degrees of collagen deposition reduction of 33.8 and 46.1%, respectively. High-resolution UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS metabolic profiling and colorimetrically polyphenolic quantification were performed for further confirmation and explanation of the represented effects. Such activity was believed to be due to the tentative identification of twenty-seven flavonoids and one phenolic acid along with a phenolic content of 57.8 mg/gm (gallic acid equivalent) and flavonoid content of 22.5 mg/gm (quercetin equivalent). Conclusion: Dinebra retroflexa may be considered as a promising anti-fibrotic agent for people at high risk of complicated lung fibrosis. The results proved that further clinical trials would be recommended to confirm the proposed findings.
Keywords: Dinebra retroflexa; UHPLC/QTOF-MS/MS; bleomycin; pulmonary fibrosis; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sharaf Y.A., El Deeb S., Ibrahim A.E., Al-Harrasi A., Sayed R.A. Two Green Micellar HPLC and Mathematically Assisted UV Spectroscopic Methods for the Simultaneous Determination of Molnupiravir and Favipiravir as a Novel Combined COVID-19 Antiviral Regimen. Molecules. 2022;27:2330. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072330. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dudala S.S., Venkateswarulu T., Kancharla S.C., Kodali V.P., Babu D.J. A review on importance of bioactive compounds of medicinal plants in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (special emphasis on isoquinoline alkaloids) Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021;7:156. doi: 10.1186/s43094-021-00304-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

