A Novel Methodology for Classifying EMG Movements Based on SVM and Genetic Algorithms
- PMID: 36557408
- PMCID: PMC9781991
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13122108
A Novel Methodology for Classifying EMG Movements Based on SVM and Genetic Algorithms
Abstract
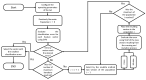
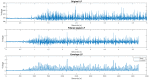
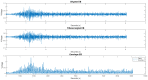
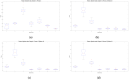
Electromyography (EMG) processing is a fundamental part of medical research. It offers the possibility of developing new devices and techniques for the diagnosis, treatment, care, and rehabilitation of patients, in most cases non-invasively. However, EMG signals are random, non-stationary, and non-linear, making their classification difficult. Due to this, it is of vital importance to define which factors are helpful for the classification process. In order to improve this process, it is possible to apply algorithms capable of identifying which features are most important in the categorization process. Algorithms based on metaheuristic methods have demonstrated an ability to search for suitable subsets of features for optimization problems. Therefore, this work proposes a methodology based on genetic algorithms for feature selection to find the parameter space that offers the slightest classification error in 250 ms signal segments. For classification, a support vector machine is used. For this work, two databases were used, the first corresponding to the right upper extremity and the second formed by movements of the right lower extremity. For both databases, a feature space reduction of over 65% was obtained, with a higher average classification efficiency of 91% for the best subset of parameters. In addition, particle swarm optimization (PSO) was applied based on right upper extremity data, obtaining an 88% average error and a 46% reduction for the best subset of parameters. Finally, a sensitivity analysis was applied to the characteristics selected by PSO and genetic algorithms for the database of the right upper extremity, obtaining that the parameters determined by the genetic algorithms show greater sensitivity for the classification process.
Keywords: electromyography; feature selection; metaheuristic algorithms; pattern recognition; support vector machine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Identification of a feature selection based pattern recognition scheme for finger movement recognition from multichannel EMG signals.Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2018 Jun;41(2):549-559. doi: 10.1007/s13246-018-0646-7. Epub 2018 May 9. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2018. PMID: 29744809
-
An Efficient Feature Selection Strategy Based on Multiple Support Vector Machine Technology with Gene Expression Data.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Aug 30;2018:7538204. doi: 10.1155/2018/7538204. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30228989 Free PMC article.
-
A mechatronics platform to study prosthetic hand control using EMG signals.Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2016 Sep;39(3):765-71. doi: 10.1007/s13246-016-0458-6. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2016. PMID: 27278475
-
Review on electromyography based intention for upper limb control using pattern recognition for human-machine interaction.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2022 May;236(5):628-645. doi: 10.1177/09544119221074770. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2022. PMID: 35118907 Review.
-
Surface electromyography signal processing and classification techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Sep 17;13(9):12431-66. doi: 10.3390/s130912431. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24048337 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repeatability and Temporal Consistency of Lower Limb Biomechanical Variables Expressing Interlimb Coordination during the Double-Support Phase in People with and without Stroke Sequelae.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;23(5):2526. doi: 10.3390/s23052526. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904730 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Effects of a Focal Muscle Vibration Protocol on Sensorimotor Integration in Healthy Subjects.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 15;13(4):664. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040664. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190629 Free PMC article.
-
Knee Angle Estimation from Surface EMG during Walking Using Attention-Based Deep Recurrent Neural Networks: Feasibility and Initial Demonstration in Cerebral Palsy.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;24(13):4217. doi: 10.3390/s24134217. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39000996 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle Tone Assessment by Machine Learning Using Surface Electromyography.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;24(19):6362. doi: 10.3390/s24196362. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409402 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern Recognition in the Processing of Electromyographic Signals for Selected Expressions of Polish Sign Language.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;24(20):6710. doi: 10.3390/s24206710. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toledo-Pérez D.C., Rodríguez-Reséndiz J., Gómez-Loenzo R.A., Jauregui-Correa J.C. Support Vector Machine-based EMG signal classification techniques: A review. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:4402. doi: 10.3390/app9204402. - DOI
-
- Kehri V., Awale R. EMG Signal Analysis for Diagnosis of Muscular Dystrophy Using Wavelet Transform, SVM and ANN. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2018;11:1583–1591. doi: 10.13005/bpj/1525. - DOI
-
- Dhindsa I.S., Agarwal R., Ryait H.S. Performance evaluation of various classifiers for predicting knee angle from electromyography signals. Expert Syst. 2019;36:e12381. doi: 10.1111/exsy.12381. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

