Battery-Free Tattooing Mechanism-Based Functional Active Capsule Endoscopy
- PMID: 36557410
- PMCID: PMC9786073
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13122111
Battery-Free Tattooing Mechanism-Based Functional Active Capsule Endoscopy
Abstract
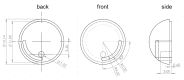
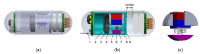
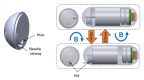
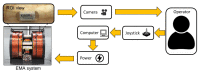
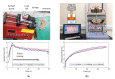
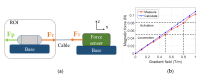
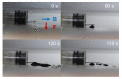
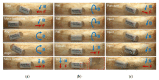
This paper presents a novel tattooing capsule endoscope (TCE) for delivering a certain amount of ink to the submucosal layer of digestive tract organs. A dual-function permanent magnet is used for locomotion and injection activation. The developed capsule endoscope can move actively in 5 DOF due to the interaction between the permanent magnet and a controllable external magnetic field produced by an electromagnet actuation system. In addition, the permanent magnet is involved in a specially designed mechanism to activate a process that creates a squeezing motion to eject the liquid from the storage room to the target. The dimension of the prototype is 12.5 mm in diameter and 34.6 mm in length. The proposed TCE is tested ex vivo using a fresh porcine small-intestine segment. We were able to direct the TCE to the target and deliver the tattoo agent into the tissue. The proposed mechanism can be used for drug delivery or lesion tattooing, as well as to accelerate the realization of the functional capsule endoscope in practice.
Keywords: active capsule endoscope; gastrointestinal tract diagnosis; tattooing function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

