Imaging of Musculoskeletal Soft-Tissue Infections in Clinical Practice: A Comprehensive Updated Review
- PMID: 36557582
- PMCID: PMC9784663
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10122329
Imaging of Musculoskeletal Soft-Tissue Infections in Clinical Practice: A Comprehensive Updated Review
Abstract
Musculoskeletal soft-tissue infections include a wide range of clinical conditions that are commonly encountered in both emergency departments and non-emergency clinical settings. Since clinical signs, symptoms, and even laboratory tests can be unremarkable or non-specific, imaging plays a key role in many cases. MRI is considered the most comprehensive and sensitive imaging tool available for the assessment of musculoskeletal infections. Ultrasound is a fundamental tool, especially for the evaluation of superficially located diseases and for US-guided interventional procedures, such as biopsy, needle-aspiration, and drainage. Conventional radiographs can be very helpful, especially for the detection of foreign bodies and in cases of infections with delayed diagnosis displaying bone involvement. This review article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the radiological tools available and the imaging features of the most common musculoskeletal soft-tissue infections, including cellulitis, necrotizing and non-necrotizing fasciitis, foreign bodies, abscess, pyomyositis, infectious tenosynovitis, and bursitis.
Keywords: interventional; magnetic resonance imaging; multidetector computed tomography; radiography; soft tissue infections; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
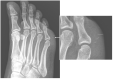
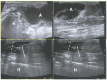
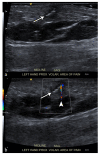
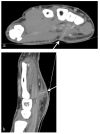
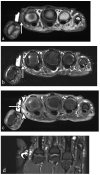
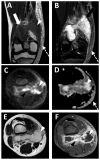
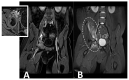
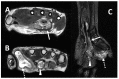
Similar articles
-
Imaging of musculoskeletal soft tissue infections.Skeletal Radiol. 2010 Oct;39(10):957-71. doi: 10.1007/s00256-009-0780-0. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Skeletal Radiol. 2010. PMID: 19714328 Review.
-
Musculoskeletal infections: ultrasound appearances.Clin Radiol. 2005 Feb;60(2):149-59. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2004.02.005. Clin Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15664569 Review.
-
High-resolution ultrasound in the evaluation of musculoskeletal infections.J Ultrason. 2023 Nov 23;23(95):e272-e284. doi: 10.15557/jou.2023.0034. eCollection 2023 Oct. J Ultrason. 2023. PMID: 38020512 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonography of musculoskeletal infections in children.Eur Radiol. 2004 Mar;14 Suppl 4:L65-77. doi: 10.1007/s00330-003-2029-y. Eur Radiol. 2004. PMID: 14752567 Review.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of musculoskeletal infections.Pol J Radiol. 2022 Mar 5;87:e141-e162. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2022.113825. eCollection 2022. Pol J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35505859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complicated and deep bacterial skin and soft tissue infections.J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2025 Mar;23(3):357-375. doi: 10.1111/ddg.15493. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2025. PMID: 40052618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Application of Infrared Thermography in Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2025 Jan 30;36(2):159-192. doi: 10.31138/mjr.271024.ita. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40757122 Free PMC article.
-
Arthritis or an Adjacent Fascial Response? A Case Report of Combined Pyomyositis and Aseptic Arthritis.Case Rep Rheumatol. 2024 Jun 25;2024:2608144. doi: 10.1155/2024/2608144. eCollection 2024. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38957409 Free PMC article.
-
Musculoskeletal infections through direct inoculation.Skeletal Radiol. 2024 Oct;53(10):2161-2179. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04591-w. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Skeletal Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38291151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical presentation of polymicrobial cervicofacial necrotizing fasciitis: An extraordinary odontogenic infection in a healthy female patient.Clin Case Rep. 2024 Aug 27;12(9):e9382. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.9382. eCollection 2024 Sep. Clin Case Rep. 2024. Retraction in: Clin Case Rep. 2024 Dec 12;12(12):e9704. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.9704. PMID: 39206071 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Headley A.J. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: A primary care review. Am. Fam. Physician. 2003;68:323–328. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

