Surveillance of Legionella pneumophila: Detection in Public Swimming Pool Environment
- PMID: 36557683
- PMCID: PMC9784426
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10122429
Surveillance of Legionella pneumophila: Detection in Public Swimming Pool Environment
Abstract
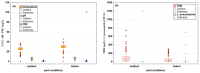
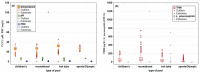
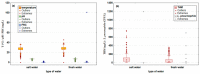
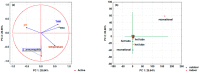
The bacterium Legionella pneumophila is a ubiquitous microorganism naturally present in water environments. The actual presence of this opportunistic premise plumbing pathogen in recreational swimming pools and hot tubs in the northwestern part of Croatia has not been investigated. This study aimed to analyze the presence of the opportunistic pathogen L. pneumophila in public swimming pool water in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County (N = 4587) over a four-year period (2018-2021). Additionally, the second aim was to investigate the connection between the presence of L. pneumophila and pool water physicochemical parameters using mathematical predictive models. The presence of L. pneumophila was detected in six pool samples. Five positive samples were found in the water of indoor hot tubs filled with fresh water, and one positive sample in an outdoor recreational saltwater pool. A predictive mathematical model showed the simultaneous influence of chemical parameters dominated by the temperature in saltwater and freshwater pools, as well as the significant influence of free residual chlorine and trihalomethanes. Our results pointed out that keeping all physicochemical parameters in perfect harmony is necessary to reach the best disinfection procedure and to avoid the optimum conditions for L. pneumophila occurrence.
Keywords: Legionella spp.; physicochemical parameters; prevention; recreational water; swimming pool water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of temperature, chlorine residual and heavy metals on the presence of Legionella pneumophila in hot water distribution systems.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2012;19(3):431-6. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2012. PMID: 23020035
-
[Legionella pneumophila in pool water].Ugeskr Laeger. 2000 Jun 19;162(25):3592-4. Ugeskr Laeger. 2000. PMID: 11016282 Danish.
-
Is a Proactive Approach to Controlling Legionella in the Environment Justified?Food Technol Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;59(3):314-324. doi: 10.17113/ftb.59.03.21.7016. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34759763 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella Occurrence beyond Cooling Towers and Premise Plumbing.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 9;9(12):2543. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122543. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34946143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Legionella pneumophila: The Paradox of a Highly Sensitive Opportunistic Waterborne Pathogen Able to Persist in the Environment.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 8;7:486. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00486. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27092135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018. ECDC; Stockholm, Sweden: 2020. [(accessed on 30 October 2022)]. Legionnaires’ disease. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AER_for_2018_Le....
-
- Del Piano M., La Palombara P., Nicosia R., Picchiotti R. The legionellosis. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1984;63:87–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

