Efficient Degradation of Congo Red in Water by UV-Vis Driven CoMoO4/PDS Photo-Fenton System
- PMID: 36557777
- PMCID: PMC9784357
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27248642
Efficient Degradation of Congo Red in Water by UV-Vis Driven CoMoO4/PDS Photo-Fenton System
Abstract
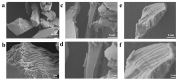
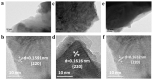
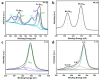
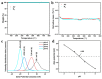
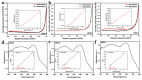
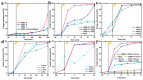
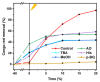
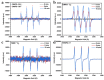
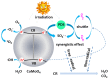
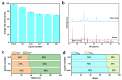
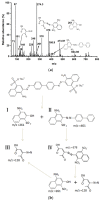
In order to improve the catalytic activity of cobalt molybdate (CoMoO4), a PDS-activated and UV-vis assisted system was constructed. CoMoO4 was prepared by coprecipitation and calcination, and characterized by XRD, FTIR, Raman, SEM, TEM, XPS, TGA Zeta potential, BET, and UV-Vis DRS. The results showed that the morphology of the CoMoO4 nanolumps consisted of stacked nanosheets. XRD indicated the monoclinic structures with C2/m (C32h, #12) space group, which belong to α-CoMoO4, and both Co2+ and Mo6+ ions occupy distorted octahedral sites. The pH of the isoelectric point (pHIEP) of CMO-8 at pH = 4.88 and the band gap of CoMoO4 was 1.92 eV. The catalytic activity of CoMoO4 was evaluated by photo-Fenton degradation of Congo red (CR). The catalytic performance was affected by calcination temperature, catalyst dosage, PDS dosage, and pH. Under the best conditions (0.8 g/L CMO-8, PDS 1 mL), the degradation efficiency of CR was 96.972%. The excellent catalytic activity of CoMoO4 was attributed to the synergistic effect of photo catalysis and CoMoO4-activated PDS degradation. The capture experiments and the ESR showed that superoxide radical (·O2-), singlet oxygen (1O2), hole (h+), sulfate (SO4-·), and hydroxyl (·OH-) were the main free radicals leading to the degradation of CR. The results can provide valuable information and support for the design and application of high-efficiency transition metal oxide catalysts.
Keywords: CoMoO4; Congo red; PDS; photo-Fenton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Haounati R., Alakhras F., Ouachtak H., Saleh T., Al-Mazaideh G., Alhajri E., Jada A., Hafid N., Addi A. Synthesized of Zeolite@Ag2O Nanocomposite as Superb Stability Photocatalysis Toward Hazardous Rhodamine B Dye from Water. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022;2022:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s13369-022-06899-y. - DOI
-
- Haounati R., El Guerdaoui A., Ouachtak H., El Haouti R., Bouddouch A., Hafid N., Bakiz B., Santos D.M.F., Taha M.L., Jada A., et al. Design of direct Z-scheme superb magnetic nanocomposite photocatalyst Fe3O4/Ag3PO4@Sep for hazardous dye degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021;277:119399.
-
- Das T., Ganguly S., Bhawal1 P., Mondal1 S., Das N. A facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticle-decorated hydroxyapatite for efficient catalytic activity towards 4-nitrophenol reduction. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018;44:1189–1208. doi: 10.1007/s11164-017-3161-7. - DOI
-
- Das T., Remanan S., Ghosh S., Ghosh S., Das N. Efficient synthesis of catalytic active silver nanoparticles illuminated cerium oxide nanotube: A mussel inspired approach. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021;15:100411. doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100411. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

