Mediterranean Food Industry By-Products as a Novel Source of Phytochemicals with a Promising Role in Cancer Prevention
- PMID: 36557789
- PMCID: PMC9784942
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27248655
Mediterranean Food Industry By-Products as a Novel Source of Phytochemicals with a Promising Role in Cancer Prevention
Abstract
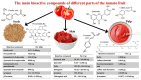
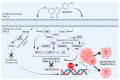
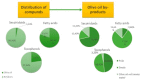
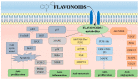
The Mediterranean diet is recognized as a sustainable dietary approach with beneficial health effects. This is highly relevant, although the production of typical Mediterranean food, i.e., olive oil or wine, processed tomatoes and pomegranate products, generates significant amounts of waste. Ideally, this waste should be disposed in an appropriate, eco-friendly way. A number of scientific papers were published recently showing that these by-products can be exploited as a valuable source of biologically active components with health benefits, including anticancer effects. In this review, accordingly, we elaborate on such phytochemicals recovered from the food waste generated during the processing of vegetables and fruits, typical of the Mediterranean diet, with a focus on substances with anticancer activity. The molecular mechanisms of these phytochemicals, which might be included in supporting treatment and prevention of various types of cancer, are presented. The use of bioactive components from food waste may improve the economic feasibility and sustainability of the food processing industry in the Mediterranean region and can provide a new strategy to approach prevention of cancer.
Keywords: Mediterranean food industry; anticancer activity; by-products; cancer; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioactive potential of fruit and vegetable wastes.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2020;91:157-225. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.07.001. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2020. PMID: 32035596 Review.
-
Fruit Wastes as a Valuable Source of Value-Added Compounds: A Collaborative Perspective.Molecules. 2021 Oct 20;26(21):6338. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216338. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770747 Free PMC article.
-
Mediterranean Food By-products as a Valuable Source of Bioactive Compounds with Health Properties.Curr Med Chem. 2024 Jul 25. doi: 10.2174/0109298673309549240723054831. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39069712
-
The Mediterranean Diet as source of bioactive compounds with multi-targeting anti-cancer profile.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 1;181:111579. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111579. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31398616 Review.
-
Mediterranean products as promising source of multi-target agents in the treatment of metabolic syndrome.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 15;186:111903. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111903. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31787360 Review.
Cited by
-
From Orchard to Wellness: Unveiling the Health Effects of Sweet Cherry Nutrients.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 28;16(21):3660. doi: 10.3390/nu16213660. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of Germinated Seeds as Functional Food Ingredients: Optimization of Nutrient Composition and Antioxidant Activity Evolution Based on the Germination Characteristics of Chinese Chestnut (Castanea mollissima).Foods. 2024 Aug 20;13(16):2605. doi: 10.3390/foods13162605. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200532 Free PMC article.
-
Valorization of Olive Oil and Wine Industry Byproducts: Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainable Food Applications.Foods. 2025 Jul 15;14(14):2475. doi: 10.3390/foods14142475. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Healthy Lifestyle and Cancer Risk: Modifiable Risk Factors to Prevent Cancer.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 11;16(6):800. doi: 10.3390/nu16060800. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactivity and Bioavailability of Carotenoids Applied in Human Health: Technological Advances and Innovation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 11;25(14):7603. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147603. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Machado A.P.d.F., Geraldi M.V., do Nascimento R.d.P., Moya A.M.T.M., Vezza T., Diez-Echave P., Gálvez J.J., Cazarin C.B.B., Maróstica Júnior M.R. Polyphenols from Food By-Products: An Alternative or Complementary Therapy to IBD Conventional Treatments. Food Res. Int. 2021;140:110018. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.110018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

