Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity
- PMID: 36557979
- PMCID: PMC9783495
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27248849
Deamination of 1-Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids: Reaction Intermediates and Selectivity
Abstract
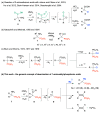
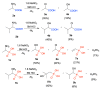
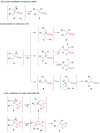
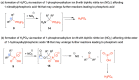
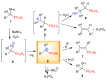
Deamination of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids in the reaction with HNO2 (generated "in situ" from NaNO2) yields a mixture of substitution products (1-hydroxyalkylphosphonic acids), elimination products (vinylphosphonic acid derivatives), rearrangement and substitution products (2-hydroxylkylphosphonic acids) as well as H3PO4. The variety of formed reaction products suggests that 1-phosphonoalkylium ions may be intermediates in such deamination reactions.
Keywords: 1-phosphonoalkylium ion; carbenium ion; diazotization; elimination reaction; rearrangement; substitution reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Use of Phenols as Nucleophiles in the Zbiral Oxidative Deamination of N-Acetyl Neuraminic Acid: Isolation and Characterization of Tricyclic 3-Keto-2-deoxy-nonulosonic Acid (KDN) Derivatives via an Intermediate Vinyl Diazonium Ion.J Org Chem. 2019 Nov 15;84(22):14688-14700. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b02279. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Org Chem. 2019. PMID: 31608634 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and stability of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acid quaternary ammonium salts.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Jul 28;19(29):6422-6430. doi: 10.1039/d1ob00703c. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34018544
-
Dehydration versus deamination of N-terminal glutamine in collision-induced dissociation of protonated peptides.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007 Jan;18(1):27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2006.08.016. Epub 2006 Sep 26. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007. PMID: 17005415
-
Metabolism of branched-chain amino acids and ammonia during exercise: clues from McArdle's disease.Int J Sports Med. 1990 May;11 Suppl 2:S101-13. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1024861. Int J Sports Med. 1990. PMID: 2193889 Review.
-
[NO-dependent modifications of nucleic acids].Bioorg Khim. 2007 Mar-Apr;33(2):195-228. doi: 10.1134/s106816200702001x. Bioorg Khim. 2007. PMID: 17476982 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Special Issue "Organophosphorus Chemistry: A New Perspective".Molecules. 2023 Jun 14;28(12):4752. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124752. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375307 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

