Therapeutic Importance of Kaempferol in the Treatment of Cancer through the Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways
- PMID: 36557997
- PMCID: PMC9788613
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27248864
Therapeutic Importance of Kaempferol in the Treatment of Cancer through the Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways
Abstract
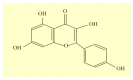
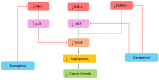
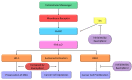
Plant-derived flavonoids are considered natural nontoxic chemo-preventers and have been widely studied for cancer treatment in recent decades. Mostly all flavonoid compounds show significant anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antioxidant properties. Kaempferol (Kmp) is a well-studied compound and exhibits remarkable anticancer and antioxidant potential. Kmp can regulate various cancer-related processes and activities such as cell cycle, oxidative stress, apoptosis, proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis. The anti-cancer properties of Kmp primarily occur via modulation of apoptosis, MAPK/ERK1/2, P13K/Akt/mTOR, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signalling pathways. The anti-cancer property of Kmp has been recognized in several in-vivo and in-vitro studies which also includes numerous cell lines and animal models. This flavonoid possesses toxic activities against only cancer cells and have restricted toxicity on healthy cells. In this review, we present extensive research investigations about the therapeutic potential of Kmp in the management of different types of cancers. The anti-cancer properties of Kmp are discussed by concentration on its capability to target molecular-signalling pathway such as VEGF, STAT, p53, NF-κB and PI3K-AKT signalling pathways. The anti-cancer property of Kmf has gained a lot of attention, but the accurate action mechanism remains unclear. However, this natural compound has a great pharmacological capability and is now considered to be an alternative cancer treatment.
Keywords: anti-cancer activity; anti-inflammatory; cell signalling pathways; flavonoids; kaempferol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential Therapeutic Targets of Quercetin, a Plant Flavonol, and Its Role in the Therapy of Various Types of Cancer through the Modulation of Various Cell Signaling Pathways.Molecules. 2021 Mar 1;26(5):1315. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051315. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33804548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol inhibits angiogenic ability by targeting VEGF receptor-2 and downregulating the PI3K/AKT, MEK and ERK pathways in VEGF-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 May;39(5):2351-2357. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6312. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29565448
-
Anticancer Properties of Kaempferol on Cellular Signaling Pathways.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(30):2474-2482. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220907112822. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36082856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cells by Inducing Apoptosis and Autophagy via Inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Anticancer Res. 2024 Jul;44(7):2961-2972. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17108. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38925830
-
Kaempferol Attenuates Myocardial Ischemic Injury via Inhibition of MAPK Signaling Pathway in Experimental Model of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7580731. doi: 10.1155/2016/7580731. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27087891 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chitosan-loaded piperlongumine nanoparticles and kaempferol enhance the anti-cancer action of doxorubicin in targeting of Ehrlich solid adenocarcinoma: in vivo and in silico modeling study.Med Oncol. 2024 Jan 23;41(2):61. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02282-5. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38253759 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of kaempferol in digestive system tumors: recent advances and mechanistic insights.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 15;15(1):658. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01510-2. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39546109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echis ocellatus venom-induced sperm functional deficits, pro-apoptotic and inflammatory activities in male reproductive organs in rats: antagonistic role of kaempferol.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 9;25(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00776-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39123263 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of Laurus nobilis extract by experimental and computational approaches: phenolic content and bioactivities for antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticholinergic properties.Front Chem. 2025 Feb 19;13:1541250. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1541250. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40046016 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative in silico and in vivo Drosophila model studies reveal the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties of red radish microgreen extract.Sci Rep. 2025 May 27;15(1):18533. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02999-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UICC GLOBOCAN 2020: New Global Cancer Data. [(accessed on 27 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.uicc.org/news/globocan-2020-new-global-cancer-data.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

