Effect of Esculetin on Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Oxidative Injury in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 36558102
- PMCID: PMC9781126
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27248970
Effect of Esculetin on Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Oxidative Injury in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells In Vitro
Abstract
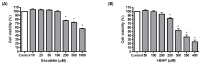
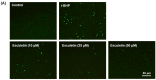
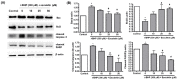
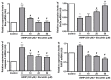
Esculetin is a coumarin-derived compound with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The current study aims to evaluate the therapeutic implications of esculetin on retinal dysfunction and uncover the underlying mechanisms. Tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) at a concentration of 300 μM was used to induce oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cell line (ARPE-19) cells. Esculetin at concentrations below 250 μM did not cause cytotoxicity to ARPE-19 cells. Cell viability analysis confirmed that t-BHP induced oxidative injury of ARPE-19 cells. However, ARPE-19 cells were protected from t-BHP-induced oxidative injury by esculetin in a concentration-dependent manner. As a result of the TUNEL assay to confirm apoptosis, esculetin treatment reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells. Esculetin down-regulated the expression levels of Bax, Caspase-3, and PARP and up-regulated the expression level of Bcl2. Collectively, this study demonstrates that esculetin exerts potent antioxidant properties in ARPE-19 cells, inhibiting t-BHP-induced apoptosis under the regulation of apoptotic factors.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; apoptosis; esculetin; oxidative stress; retinal pigment epithelial cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zarbin M.A., Casaroli-Marano R.P., Rosenfeld P.J. Age-related macular degeneration: Clinical findings, histopathology and imaging techniques. Cell-Based Ther. Retin. Degener. Dis. 2014;53:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Eyetech Study G. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for subfoveal choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration: Phase II study results. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:979–986. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

