Screening and Structure-Activity Relationship for Selective and Potent Anti-Melanogenesis Agents Derived from Species of Mulberry (Genus Morus)
- PMID: 36558142
- PMCID: PMC9783946
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27249011
Screening and Structure-Activity Relationship for Selective and Potent Anti-Melanogenesis Agents Derived from Species of Mulberry (Genus Morus)
Abstract
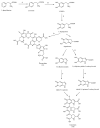
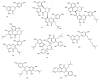
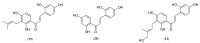
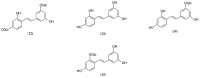
Tyrosinase is a multifunctional, copper-containing and rate-limiting oxidase that catalyses crucial steps in the melanogenesis pathway and is responsible for skin-pigmentation abnormalities in mammals. Numerous tyrosinase inhibitors derived from natural and synthetic sources have been identified as an objective for the development of anti-melanogenesis agents. However, due to side effects and lack of expected efficiency, only a small percentage of them are used for medical and cosmetic purposes. This critical review focuses on searching for novel active substances and recently discovered plant-derived anti-tyrosinase inhibitors from the Morus genus (Moraceae family). A detailed analysis of their structure-activity relationships is discussed. The information contained in this article is crucial for the cosmetics and medical industries, in order to show new directions for the effective search for natural anti-melanogenesis products (with satisfactory efficiency and safety) to treat and cure hyperpigmentation.
Keywords: genus Morus; hyperpigmentation; tyrosinase inhibitors; tyrosine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of Melanogenesis Inhibitory Constituents of Morus alba Leaves and Optimization of Extraction Conditions Using Response Surface Methodology.Molecules. 2015 May 14;20(5):8730-41. doi: 10.3390/molecules20058730. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26007176 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Melanogenic Properties of Greek Plants. A Novel Depigmenting Agent from Morus alba Wood.Molecules. 2017 Mar 23;22(4):514. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040514. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28333105 Free PMC article.
-
An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 May 26;10(6):2440-2475. doi: 10.3390/ijms10062440. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19582213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Tyrosinase Inhibitors from Plant Source.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(18):3279-3299. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180522091311. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29788869 Review.
-
Moraceae Plants with Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity: A Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(2):108-121. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160609071854. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27292779 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenolic acids in Panax ginseng inhibit melanin production through bidirectional regulation of melanin synthase transcription via different signaling pathways.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Nov;47(6):714-725. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.05.002. Epub 2023 May 28. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 38107393 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin 3-O-(6″-O-E-caffeoyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside, a Flavonoid Compound, Promotes Melanogenesis through the Upregulation of MAPKs and Akt/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4780. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054780. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali S.A., Choudhary R.K., Naaz I., Ali A.S. Understanding the challenges of melanogenesis: Key role of bioactive compounds in the treatment of hyperpigmentory disorders. J. Pigment. Disord. 2015;2:1000223. doi: 10.4172/2376-0427.1000223. - DOI
-
- Jin K.S., Oh Y.N., Hyun S.K., Kwon H.J., Kim B.W. Betulinic acid isolated from Vitis amurensis root inhibits 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine induced melanogenesis via the regulation of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in B16F10 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014;68:38–43. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.03.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

