The Potential Role of Fisetin, a Flavonoid in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
- PMID: 36558146
- PMCID: PMC9782831
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27249009
The Potential Role of Fisetin, a Flavonoid in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
Abstract
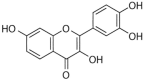
Cancer is a main culprit and the second-leading cause of death worldwide. The current mode of treatment strategies including surgery with chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be effective, but cancer is still considered a major cause of death. Plant-derived products or their purified bioactive compounds have confirmed health-promoting effects as well as cancer-preventive effects. Among these products, flavonoids belong to polyphenols, chiefly found in fruits, vegetables and in various seeds/flowers. It has been considered to be an effective antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and to play a vital role in diseases management. Besides these activities, flavonoids have been revealed to possess anticancer potential through the modulation of various cell signaling molecules. In this regard, fisetin, a naturally occurring flavonoid, has a confirmed role in disease management through antioxidant, neuro-protective, anti-diabetic, hepato-protective and reno-protective potential. As well, its cancer-preventive effects have been confirmed via modulating various cell signaling pathways including inflammation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, growth factor, transcription factor and other cell signaling pathways. This review presents an overview of the anti-cancer potential of fisetin in different types of cancer through the modulation of cell signaling pathways based on in vivo and in vitro studies. A synergistic effect with anticancer drugs and strategies to improve the bioavailability are described. More clinical trials need to be performed to explore the anti-cancer potential and mechanism-of-action of fisetin and its optimum therapeutic dose.
Keywords: bioavailability; cancer; cell signaling pathways; fisetin; synergistic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Potential and Molecular Mechanisms of the Multitargeted Flavonoid Fisetin.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(21):2075-2096. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230710162217. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37431899 Review.
-
Fisetin, a Potent Anticancer Flavonol Exhibiting Cytotoxic Activity against Neoplastic Malignant Cells and Cancerous Conditions: A Scoping, Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 23;14(13):2604. doi: 10.3390/nu14132604. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807785 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin: A Significant Emphasis on Its Anticancer Potential via the Modulation of Inflammation and Signal Transduction Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 2;24(11):9665. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119665. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The flavonoid fisetin as an anticancer agent targeting the growth signaling pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 15;789:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27377217 Review.
-
Fisetin: A bioactive phytochemical with potential for cancer prevention and pharmacotherapy.Life Sci. 2018 Feb 1;194:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.005. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29225112 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive view on the fisetin impact on colorectal cancer in animal models: Focusing on cellular and molecular mechanisms.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Oct;7(5):591-605. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12476. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39136058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Plant-Derived Natural Products as a Regulator of the Tyrosine Kinase Pathway in the Management of Lung Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 30;47(7):498. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070498. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Interactions of Flavonoids with the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor In Silico and Their Impact on Receptor Activity In Vitro.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;17(8):980. doi: 10.3390/ph17080980. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204085 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol and Fisetin-Related Signaling Pathways Induce Apoptosis in Head and Neck Cancer Cells.Cells. 2023 Jun 6;12(12):1568. doi: 10.3390/cells12121568. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371038 Free PMC article.
-
Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes for Toxins Sensing in Environmental Samples-A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;25(7):2339. doi: 10.3390/s25072339. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Devi K.P., Rajavel T., Nabavi S.F., Setzer W.N., Ahmadi A., Mansouri K. Hesperidin: A promising anticancer agent from nature. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015;76:582–589. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.07.051. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

