Variation of Saponins in Sanguisorba officinalis L. before and after Processing (Paozhi) and Its Effects on Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 36558181
- PMCID: PMC9785891
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27249046
Variation of Saponins in Sanguisorba officinalis L. before and after Processing (Paozhi) and Its Effects on Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro
Abstract
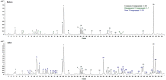
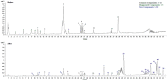
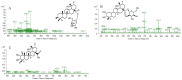
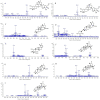
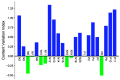
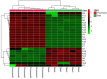
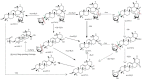
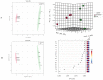
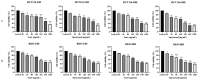
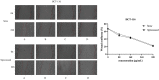
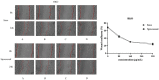
The incidence of colon cancer is increasing year over year, seriously affecting human health and quality of life in recent years. However, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been utilized for the treatment of colon cancer. S. officinalis Saponins (S-Saponins), the potential compound of TCM, displays multiple biological activities in colon cancer treatment. In our study, ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) combined with multivariate statistical analysis were performed to analyze and identify raw and processed saponins. Then, MTT and cell migration assays were used to preliminarily explore the effects of saponins in vitro on colon cancer cells. The results showed that 29 differential saponins compounds under Paozhi were identified by UHPLC-MS/MS. Moreover, in vitro validation showed that Sprocessed better inhibited the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells than Sraw. This study provides a basis for the determination of the chemical fundamentals of the efficacy changes during Paozhi through inferring the changes in saponin components and its possible transformation mechanisms before and after processing S. officinalis. Meanwhile, it also provides new insights into potential bioactive ingredients for the treatment of colon cancer.
Keywords: UHPLC-MS/MS; activity study; content determination; potential ingredients; qualitative analysis; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pallag A., Roşca E., Tit D.M., MuŢiu G., Bungău S.G., Pop O.L. Monitoring the effects of treatment in colon cancer cells using immunohistochemical and histoenzymatic techniques. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. Rev. Roum. Morphol. Embryol. 2015;56:1103–1109. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019, No. 5/Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program
- No. 1573551/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. LC2015031/Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province
- No. 018RCD03/Excellent Innovative Talents Support Program of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine
- No. LBHQ16214/Project of Heilongjiang Province post-doctoral grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

