Factors That Influence the Sustainability of Human Milk Donation to Milk Banks: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36558411
- PMCID: PMC9785923
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245253
Factors That Influence the Sustainability of Human Milk Donation to Milk Banks: A Systematic Review
Abstract
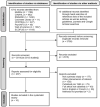
Donor human milk is the recommended alternative for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants when the mother's own milk is unavailable or not in sufficient quantity. Globally, the needs of vulnerable infants for donor human milk exceed the supply. This review aimed to identify the factors impacting the sustainability of human milk donation to milk banks. A systematic review of the literature was performed on eight databases to retrieve articles published until December 2021. The study protocol is available in PROSPERO (#CRD42021287087). Among the 6722 references identified, 10 studies (eight quantitative observational and two qualitative) met the eligibility criteria for a total of 7053 participants. Thirty factors influencing the sustainability of the donations to milk banks were identified and categorized as follows: (1) donation duration, (2) donors' infant features (e.g., gestational age, birth weight), (3) donors' features (e.g., socio-demographic characteristics, milk donation history), and (4) factors related to the milk bank and health care systems (awareness and support). The available evidence suggests that larger volumes of donated milk are associated with a longer duration of donation, as are early donation, previous milk donation, and donors with an infant of smaller weight and gestational age. Supporting and encouraging early donation and recruiting donors with infants of low birth weight and low gestational age could support longer donation times and greater volumes of milk donated. To identify efficient strategies and to draw appropriate recommendations to improve donor milk access, future studies should further explore the issues of the sustainability of human milk donation to milk banks.
Keywords: donation sustainability; donor human milk; human milk banks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Donate or Not to Donate-Willingness to Donate and Accept Donor Human Milk.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 18;17(14):2359. doi: 10.3390/nu17142359. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732983 Free PMC article.
-
Formula versus donor breast milk for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 20;6(6):CD002971. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002971.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jul 19;7:CD002971. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002971.pub5. PMID: 29926476 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Formula milk versus donor breast milk for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD002971. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002971.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 22;(4):CD002971. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002971.pub3. PMID: 17943776 Updated.
-
Early erythropoietin for preventing red blood cell transfusion in preterm and/or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jul 19;(3):CD004863. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004863.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD004863. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004863.pub3. PMID: 16856062 Updated.
-
Formula milk versus term human milk for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(4):CD002971. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002971. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD002971. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002971.pub2. PMID: 11687169 Updated.
Cited by
-
Donor and newborn profiles and their influence on donation volume and duration: a cross-sectional study in a Spanish human milk bank.Int Breastfeed J. 2024 Aug 5;19(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13006-024-00661-w. Int Breastfeed J. 2024. PMID: 39103933 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with the Prolonged Use of Donor Human Milk at the Da Nang Hospital for Women and Children in Vietnam.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 22;16(24):4402. doi: 10.3390/nu16244402. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39771023 Free PMC article.
-
The Unsung Heroes: The Profile of the Donor at a Southern Italian Milk Bank and Driving Factors in Human Milk Donation.Children (Basel). 2024 Dec 10;11(12):1502. doi: 10.3390/children11121502. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767931 Free PMC article.
-
Factors related to milk donation based on the theory of planned behavior in pregnant women.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):2622. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86186-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39837913 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in being able to donate human milk impacts upon maternal wellbeing: Lessons for scaling up milk bank service provision.Matern Child Nutr. 2024 Oct;20(4):e13699. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13699. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Matern Child Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38987938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding 2003. [(accessed on 10 January 2022)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9241562218.
-
- World Health Organization Guidelines on Optimal Feeding of Low Birth-Weight Infants in Low-and Middle-Income Countries 2011. [(accessed on 10 January 2022)]; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/85670. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe H., Cousens S., Oestergaard M.Z., Chou D., Moller A.-B., Narwal R., Adler A., Vera Garcia C., Rohde S., Say L., et al. National, Regional, and Worldwide Estimates of Preterm Birth Rates in the Year 2010 with Time Trends since 1990 for Selected Countries: A Systematic Analysis and Implications. Lancet. 2012;379:2162–2172. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60820-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- PATH Strengthening Human Milk Banking: A Resource Toolkit for Establishing and Integrating Human Milk Bank Programs—A Global Implementation Framework. 2019. [(accessed on 16 December 2021)]. Version 2.0. Available online: https://www.path.org/programs/maternal-newborn-child-health-and-nutritio...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous