Can Lactoferrin, a Natural Mammalian Milk Protein, Assist in the Battle against COVID-19?
- PMID: 36558432
- PMCID: PMC9782828
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245274
Can Lactoferrin, a Natural Mammalian Milk Protein, Assist in the Battle against COVID-19?
Abstract
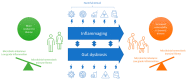
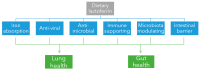
Notwithstanding mass vaccination against specific SARS-CoV-2 variants, there is still a demand for complementary nutritional intervention strategies to fight COVID-19. The bovine milk protein lactoferrin (LF) has attracted interest of nutraceutical, food and dairy industries for its numerous properties-ranging from anti-viral and anti-microbial to immunological-making it a potential functional ingredient in a wide variety of food applications to maintain health. Importantly, bovine LF was found to exert anti-viral activities against several types of viruses, including certain SARS-CoV-2 variants. LF's potential effect on COVID-19 patients has seen a rapid increase of in vitro and in vivo studies published, resulting in a model on how LF might play a role during different phases of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Aim of this narrative review is two-fold: (1) to highlight the most relevant findings concerning LF's anti-viral, anti-microbial, iron-binding, immunomodulatory, microbiota-modulatory and intestinal barrier properties that support health of the two most affected organs in COVID-19 patients (lungs and gut), and (2) to explore the possible underlying mechanisms governing its mode of action. Thanks to its potential effects on health, bovine LF can be considered a good candidate for nutritional interventions counteracting SARS-CoV-2 infection and related COVID-19 pathogenesis.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anti-viral; coronavirus; dairy; food; immunomodulation; iron-binding; lactoferrin; nutraceutical.
Conflict of interest statement
A.W.C.E is an independent nutrition consultant receiving a honorarium from Yili to write this review. The sponsor had limited involvement in preparing the manuscript, and A.W.C.E. is mainly responsible for its content. All other authors are employees of Yili.
Figures

References
-
- Ochani R.K., Asad A., Yasmin F., Shaikh S., Khalid H., Batra S., Sohail M.R., Mahmood S.F., Ochani R., Arshad M.H., et al. COVID-19 Pandemic: From Origins to Outcomes. A Comprehensive Review of Viral Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnostic Evaluation, and Management. Infez. Med. 2021;29:20–36. - PubMed
-
- Baj J., Karakuła-Juchnowicz H., Teresiński G., Buszewicz G., Ciesielka M., Sitarz R., Forma A., Karakuła K., Flieger W., Portincasa P., et al. COVID-19: Specific and Non-Specific Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms: The Current State of Knowledge. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:1753. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061753. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

