The Circadian Syndrome Is a Significant and Stronger Predictor for Cardiovascular Disease than the Metabolic Syndrome-The NHANES Survey during 2005-2016
- PMID: 36558476
- PMCID: PMC9785664
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245317
The Circadian Syndrome Is a Significant and Stronger Predictor for Cardiovascular Disease than the Metabolic Syndrome-The NHANES Survey during 2005-2016
Abstract
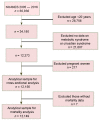
The study aimed to compare the predictive value of the Circadian Syndrome (CircS) and Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) for cardiovascular disease (CVD). We used data of 12,156 adults aged ≥20 years who attended National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2016. Mortality was obtained from the registry updated to 2019. The CircS was defined based on components of the MetS, in addition to short sleep and depression. Both the MetS and CircS were directly associated with self-reported history of CVD. The odds ratios for prevalent CVD associated with the CircS and MetS, respectively, were 2.92 (95% confidence interval (CI) 2.21-3.86) and 3.20 (2.38-4.30) in men, and 3.27 (2.34-4.59) and 3.04 (2.15-4.30) in women. The CircS had a better predictive power for prevalent CVD than that of MetS, as indicated by the higher positive predictive value (PPV); in men, the PPV for prevalent CVD with CircS was 23.1% and with MetS 20.9%, and in women these were 17.9% vs. 16.4%, respectively. However, the PPV of the CircS and MetS did not differ for the CVD mortality prediction. Women with CircS alone had a higher risk for both prevalent CVD and CVD mortality than those with MetS alone. In conclusion, the CircS is a significant and stronger predictor for CVD than the MetS in US adults.
Keywords: NHANES; adults; cardiovascular disease; circadian syndrome; metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alberti K.G., Eckel R.H., Grundy S.M., Zimmet P.Z., Cleeman J.I., Donato K.A., Fruchart J.C., James W.P., Loria C.M., Smith S.C., Jr., et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu G., Qiao Q., Tuomilehto J., Balkau B., Borch-Johnsen K., Pyorala K., Group D.S. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its relation to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in nondiabetic European men and women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004;164:1066–1076. doi: 10.1001/archinte.164.10.1066. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical