Gut Microbiota in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Complex Interplay
- PMID: 36558483
- PMCID: PMC9785319
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245323
Gut Microbiota in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Complex Interplay
Abstract
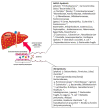
The intestinal microbiota represents the microbial community that colonizes the gastrointestinal tract and constitutes the most complex ecosystem present in nature. The main intestinal microbial phyla are Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Verrucromicrobia, with a clear predominance of the two phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes which account for about 90% of the intestinal phyla. Intestinal microbiota alteration, or dysbiosis, has been proven to be involved in the development of various syndromes, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. The present review underlines the most recurrent changes in the intestinal microbiota of patients with NAFLD, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; microbiota; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alternations of the gut microbiota and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio after biologic treatment in inflammatory bowel disease.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2025 Feb;58(1):62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2024.09.006. Epub 2024 Oct 1. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2025. PMID: 39393964
-
The Human Mesenteric Lymph Node Microbiome Differentiates Between Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.J Crohns Colitis. 2019 Jan 1;13(1):58-66. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy136. J Crohns Colitis. 2019. PMID: 30239655 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal microbial dysbiosis in Chinese patients with inflammatory bowel disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Apr 7;24(13):1464-1477. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1464. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29632427 Free PMC article.
-
Gut mycobiome: The probable determinative role of fungi in IBD patients.Mycoses. 2021 May;64(5):468-476. doi: 10.1111/myc.13238. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 33421192 Review.
-
More on the interplay between gut microbiota, autophagy, and inflammatory bowel disease is needed.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jul 21;30(27):3356-3360. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i27.3356. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39086745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Gut Microbiota: From Fatty Liver to Dysmetabolic Syndrome.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Mar 17;59(3):594. doi: 10.3390/medicina59030594. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36984595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the association between dietary fiber intake and hepatic steatosis: insights from NHANES.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 May 10;24(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03256-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38730369 Free PMC article.
-
Vegetal oil-based ketogenic diet improves inflammation and fibrosis in experimental metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 1;16:1518687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1518687. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40236713 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota in liver diseases: initiation, development and therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 4;12:1615839. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1615839. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40534699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the butyrate metabolism-related shared genes in metabolic associated steatohepatitis and ulcerative colitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 10;14(1):15949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66574-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38987612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodríguez J.M., Murphy K., Stanton C., Ross R.P., Kober O.I., Juge N., Avershina E., Rudi K., Narbad A., Jenmalm M.C., et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015;26:26050. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v26.26050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

