Effects of Different Doses, Forms, and Frequencies of Zinc Supplementation on Biomarkers of Iron and Zinc Status among Young Children in Dhaka, Bangladesh
- PMID: 36558493
- PMCID: PMC9781687
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245334
Effects of Different Doses, Forms, and Frequencies of Zinc Supplementation on Biomarkers of Iron and Zinc Status among Young Children in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Abstract
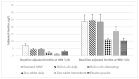
Young children in resource-constrained settings are susceptible to zinc deficiency and its deleterious health effects. The objective of this secondary analysis was to evaluate the effects of the following six interventions on biomarkers of iron and zinc status among a subgroup of young children in Dhaka, Bangladesh, who participated in the Zinc in Powders Trial (ZiPT): (1) standard micronutrient powders (MNPs) containing 4.1 mg zinc and 10 mg iron, daily; (2) high-zinc (10 mg) and low-iron (6 mg) (HiZn LoFe) MNP, daily; (3) HiZn (10 mg) and LoFe (6 mg)/HiZn (10 mg) and no-iron MNPs on alternating days; (4) dispersible zinc tablet (10 mg), daily; (5) dispersible zinc tablet (10 mg), daily for 2 weeks at enrollment and at 12 weeks; (6) placebo powder, daily. At the end of the 24 week intervention period, children in the daily dispersible zinc tablet group exhibited a mean serum zinc concentration (SZC) of 92.5 μg/dL, which was significantly higher than all other groups except the HiZn LoFe MNP alternating group (81.3 μg/dL). MNPs containing 10 mg and 6 mg of iron had a similar impact on biomarkers of iron status, with no evidence of an adverse interaction with zinc.
Keywords: Bangladesh; biomarker; micronutrients; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of Anaemia Among Young Children Receiving Daily Micronutrient Powders (MNPs) for 24 Weeks in Bangladesh: A Secondary Analysis of the Zinc in Powders Trial.Matern Child Nutr. 2025 Jul;21(3):e13806. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13806. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Matern Child Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39925177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Different Doses, Forms, and Frequencies of Zinc Supplementation for the Prevention of Diarrhea and Promotion of Linear Growth among Young Bangladeshi Children: A Six-Arm, Randomized, Community-Based Efficacy Trial.J Nutr. 2022 May 5;152(5):1306-1315. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab439. J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35015856 Clinical Trial.
-
Home fortification of foods with multiple micronutrient powders for health and nutrition in children under two years of age (Review).Evid Based Child Health. 2013 Jan;8(1):112-201. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1895. Evid Based Child Health. 2013. PMID: 23878126 Review.
-
Home fortification of foods with multiple micronutrient powders for health and nutrition in children under two years of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 28;2(2):CD008959. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008959.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32107773 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of universal iron supplementation and iron-containing micronutrient powders for anemia among young children in rural Bangladesh: analysis of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Nov;116(5):1303-1313. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac225. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36192508 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Limits of Ultra: Towards an Interdisciplinary Understanding of Ultra-Endurance Running Performance.Sports Med. 2024 Jan;54(1):73-93. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01936-8. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 37751076 Review.
-
Long-Term Impact of Multiple Micronutrient Supplementation on Micronutrient Status, Hemoglobin Level, and Growth in Children 24 to 59 Months of Age: A Non-Randomized Community-Based Trial from Pakistan.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 30;15(7):1690. doi: 10.3390/nu15071690. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049531 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sports Dietitians Australia and Ultra Sports Science Foundation Joint Position Statement: A Practitioner Guide to the Prevention and Management of Exercise-Associated Gastrointestinal Perturbations and Symptoms.Sports Med. 2025 May;55(5):1097-1134. doi: 10.1007/s40279-025-02186-6. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40195264 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of tricetin in renal cell carcinoma treatment through network pharmacology and experimental validation.Med Oncol. 2025 May 3;42(6):192. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02744-y. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40319129
-
Predictors of Anaemia Among Young Children Receiving Daily Micronutrient Powders (MNPs) for 24 Weeks in Bangladesh: A Secondary Analysis of the Zinc in Powders Trial.Matern Child Nutr. 2025 Jul;21(3):e13806. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13806. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Matern Child Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39925177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mayo-Wilson E., Junior J.A., Imdad A., Dean S., Chan X.H., Chan E.S., Jaswal A., Bhutta Z.A. Zinc supplementation for preventing mortality, morbidity, and growth failure in children aged 6 months to 12 years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014;15:CD009384. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009384.pub2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Black R.E., Victora C.G., Walker S.P., Bhutta Z.A., Christian P., de Onis M., Ezzati M., Grantham-McGregor S., Katz J., Martorell R., et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2013;382:427–451. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60937-X. - DOI - PubMed