Can Mild-to-Moderate Iodine Deficiency during Pregnancy Alter Thyroid Function? Lessons from a Mother-Newborn Cohort
- PMID: 36558495
- PMCID: PMC9781516
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245336
Can Mild-to-Moderate Iodine Deficiency during Pregnancy Alter Thyroid Function? Lessons from a Mother-Newborn Cohort
Abstract
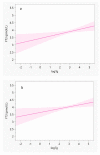
Severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy has substantial hormonal consequences, such as fetal brain damage. Data on the potential effects of mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency on the thyroid function of pregnant women and their newborns are scarce and divergent. We investigated the association between iodine intake in pregnancy and maternal and neonatal thyroid function in a region with mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency. Pregnant women’s iodine status was evaluated using an iodine food frequency questionnaire, serum thyroglobulin (Tg), and urinary iodine concentration (UIC). Neonatal thyrotropin (nTSH) values were measured after birth. Obstetrics and anthropometric data were also collected. Among the 178 women (median age 31 years) included in the study, median (interquartile range) estimated dietary iodine intake, Tg and UIC were 179 (94−268) μg/day, 18 (11−33) μg/L, and 60 (41−95) μg/L, respectively. There was a significant inverse association of iodine intake with Tg values among the study population (β = −0.2, F = 7.5, p < 0.01). Women with high free triiodothyronine (FT3) values were more likely to exhibit an estimated iodine intake below the estimated average requirement (160 μg/day, odds ratio [OR] = 2.6; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1−6.4; p = 0.04) and less likely to consume iodine-containing supplements (OR = 0.3, 95% CI, 0.1−0.8; p = 0.01). It is possible that thyroid function may be affected by iodine insufficiency during pregnancy in regions with mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency. The relatively small sample size of the studied population warrants further investigation.
Keywords: free triiodothyronine; iodine insufficiency; maternal dietary iodine intake; neonatal thyrotropin; thyroglobulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander E.K., Pearce E.N., Brent G.A., Brown R.S., Chen H., Dosiou C., Grobman W.A., Laurberg P., Lazarus J.H., Mandel S.J., et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and the Postpartum. Thyroid. 2017;27:315–389. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0457. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

