Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation in Nursing Homes-A Quality Improvement Study
- PMID: 36558519
- PMCID: PMC9780874
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14245360
Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation in Nursing Homes-A Quality Improvement Study
Abstract
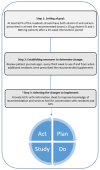
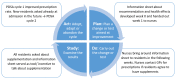
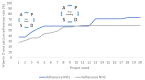
Even though dietary supplements with vitamin D and calcium are recommended to nursing home residents, we recently reported a low adherence to this recommendation. The objective of this 20-week quality improvement study was to use the Model for Improvement and Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to improve adherence in Danish nursing homes. We included two nursing homes with 109 residents at baseline. An information sheet including the rationale for the recommendation was developed for the nurses to urge residents to take the supplements and seek approval by the general practitioner afterwards (PDSA cycle 1). Moreover, it was included in admission meetings with new residents to address supplementation (PDSA cycle 2). A nurse reviewed patient records for number of residents prescribed adequate doses of vitamin D (≥20 µg) and calcium (≥800 mg) before, during and after the intervention. At baseline, 32% (n = 35) of the residents had adequate doses of vitamin D and calcium. After implementation of the information sheet and adjustment to admission meetings, this increased to 65% (n = 71) at endpoint (p < 0.001). In conclusion, in this quality improvement study, we improved the number of prescriptions of adequate doses of vitamin D and calcium over 20 weeks using the Model for Improvement and PDSA experiments.
Keywords: Model for Improvement; adherence; calcium; nursing homes; supplements; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Nordic Council of Ministers . Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012: Integrating Nutrition and Physical Activity. 1st ed. Volume 5. Norden; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2014.
-
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies) Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Vitamin D. Eur. Food Saf. Authority J. 2016;14:4547. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4547. - DOI
-
- Rolland Y., de Souto Barreto P., van Kan G.A., Annweiler C., Beauchet O., Bischoff-Ferrari H., Berrut G., Blain H., Bonnefoy M., Cesari M., et al. Vitamin D Supplementation in Older Adults: Searching for Specific Guidelines in Nursing Homes. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 2013;17:402–412. doi: 10.1007/s12603-013-0007-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Itkonen S.T., Andersen R., Björk A.K., Brugård Konde Å., Eneroth H., Erkkola M., Holvik K., Madar A.A., Meyer H.E., Tetens I., et al. Vitamin D Status and Current Policies to Achieve Adequate Vitamin D Intake in the Nordic Countries. Scand. J. Public Health. 2020;49:616–627. doi: 10.1177/1403494819896878. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

