Host tRNA-Derived RNAs Target the 3'Untranslated Region of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36558813
- PMCID: PMC9786188
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11121479
Host tRNA-Derived RNAs Target the 3'Untranslated Region of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
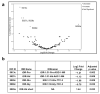
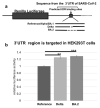
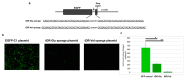
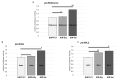
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed a need for new understanding of the mechanisms regulating host-pathogen interactions during viral infection. Transfer RNA-derived RNAs (tDRs), previously called transfer RNA fragments (tRFs), have recently emerged as potential regulators of viral pathogenesis. Many predictive studies using bioinformatic approaches have been conducted providing a repertoire of potential small RNA candidates for further analyses; however, few targets have been validated to directly bind to SARS-CoV-2 sequences. In this study, we used available data sets to identify host tDR expression altered in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. RNA-interaction-prediction tools were used to identify sequences in the SARS-CoV-2 genome where tDRs could potentially bind. We then developed luciferase assays to confirm direct regulation through a predicted region of SARS-CoV-2 by tDRs. We found that two tDRs were downregulated in both clinical and in vitro cell culture studies of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Binding sites for these two tDRs were present in the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of the SARS-CoV-2 reference virus and both sites were altered in Variants of Concern (VOCs) that emerged later in the pandemic. These studies directly confirm the binding of human tDRs to a specific region of the 3'UTR of SARS-CoV-2 providing evidence for a novel mechanism for host-pathogen regulation.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; VOCs; Variants of Concern; host-viral interactions; small noncoding RNA; tDR; tRF; tRNA fragments; tRNA-derived RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3'UTR of SARS-CoV-2 spike gene hijack host miR-296 or miR-520h to disturb cell proliferation and cytokine signaling.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 27;13:924667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.924667. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36238276 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) regulate post-transcriptional gene expression via AGO-dependent mechanism in IL-1β stimulated chondrocytes.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020 Aug;28(8):1102-1110. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.04.014. Epub 2020 May 12. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 32407895 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of tRNA-derived small noncoding RNAs as potential biomarkers for prediction of recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2018 Oct;7(10):5130-5144. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1761. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30239174 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Approaches to tRNA-Derived Small RNAs.Noncoding RNA. 2017 Jan 4;3(1):2. doi: 10.3390/ncrna3010002. Noncoding RNA. 2017. PMID: 29657274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and regulation of tRNA-derived small RNAs in animals.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 May;25(5):359-378. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00690-z. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38182846 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 remodels the landscape of small non-coding RNAs with infection time and symptom severity.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024 Apr 17;10(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41540-024-00367-z. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024. PMID: 38632240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) VOCs. [(accessed on 19 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/31-05-2021-who-announces-simple-easy-to-sa....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

